Figure 2.
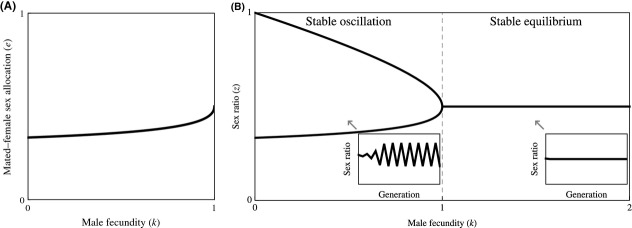
Obligate sex allocation. (A) Natural selection favors mated females to exhibit female-biased sex allocation e = (3 + k−((9−k)( 1−k))½)/(8k) when k ≤ 1 and unbiased sex allocation e = ½ when k ≥ 1. (B) This leads to stable oscillation of the sex ratio between z = (3 + k−((9−k)(1−k))½)/(8k) and z = (5−k + ((9−k)( 1−k))½)/8 when k < 1, and a stable equilibrium at z* = ½ when k ≥ 1. Insets illustrate the scenarios indicated by arrows (k = 0.50 and k = 1.50).
