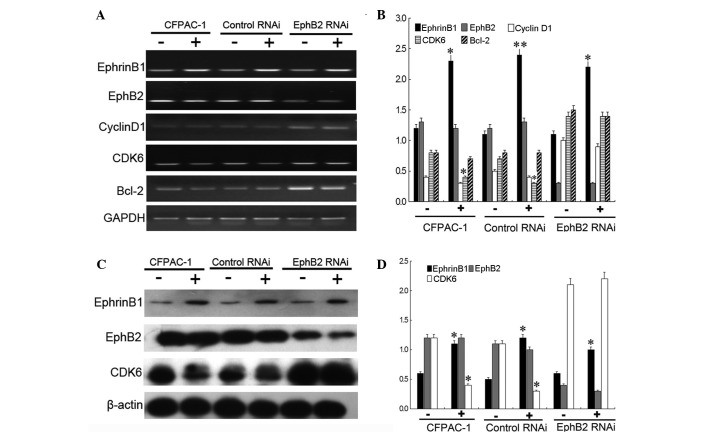
Figure 4.
High expression of EphB2 predicts a superior response to QYHJ treatment through the EphrinB1-EphB2-CDK6 pathway in CFPAC-1 cells. QYHJ resulted in an unclear change of EphB2 (A and B) mRNA and (C and D) protein level, however, a statistically significant increase was identified in the EphrinB1 (A and B) mRNA (P<0.05, P<0.01 and P<0.05) and (C and D) protein (P<0.05, P<0.05 and P<0.05) level following QYHJ treatment in CFPAC-1, CFPAC-1 control RNAi cells and CFPAC-1 EphB2 RNAi cells. QYHJ also resulted in a statistically significant decrease in the CDK6 (A and B) mRNA (P<0.05) and (C and D) protein (P<0.05) level in CFPAC-1 and CFPAC-1 control RNAi cells (P<0.05), however, no change was identified in CFPAC-1 EphB2 RNAi cells. EphB2, erythropoietin-producing hepatoma cell line-B2; QYHJ, Qingyihuaji formula; CDK6, cyclin-dependent kinase 6; EphrinB1, Eph receptor-interacting B1. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01 compared with the NS group.