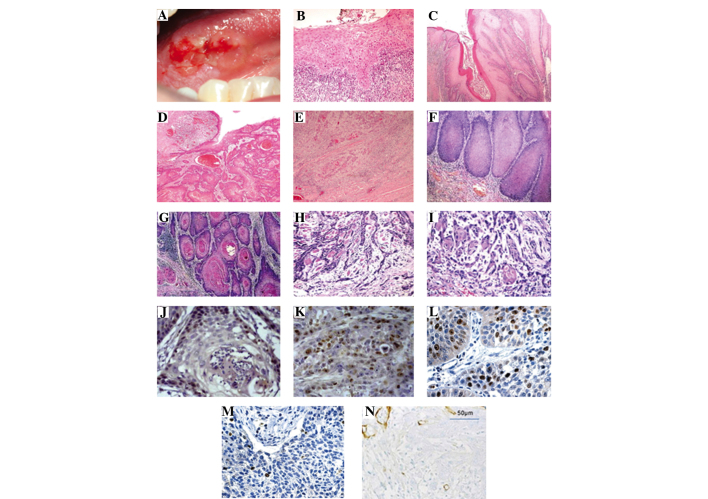
Figure 1.
(A) Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) of the lateral edge of the tongue (13). (B) Severe dysplasia of the surface epithelium associated with chronic inflammatory infiltration at the stromal-epithelial interface of the dysplastic epithelium (stain, H&E; magnification, ×50) (13). Histological grades of tumor differentiation of OSCC: (C) Well-differentiated, hyperkeratosis and inflammation associated with the stromal-epithelial interface; (D) moderately differentiated; and (E) undifferentiated infiltrating and dispersed cells with no clear demarcation between the front and surrounding tissue invasion (stain, H&E; magnification, ×25) (13). Different patterns of invasion at the tumor invasion front according to the cell morphology: (F) Wide fronts of invasion (score 1); (G) islet cell widths (score 1); (H) thin infiltrating cords (score 2); and (I) individual cells invading the interface (score 3) (1). OSCC patients (J) with recurrence and (K) without recurrence. Antibody staining for Ki-67 with a high degree of nuclear staining (magnification, ×400) (16). Representative samples of homeobox protein, HOXB7 immunohistochemical expression in OSCC with (L) high and (M) low expression (32). (N) Immunohistochemical expression of type IV collagen α2 chain in undifferentiated OSCC (38).