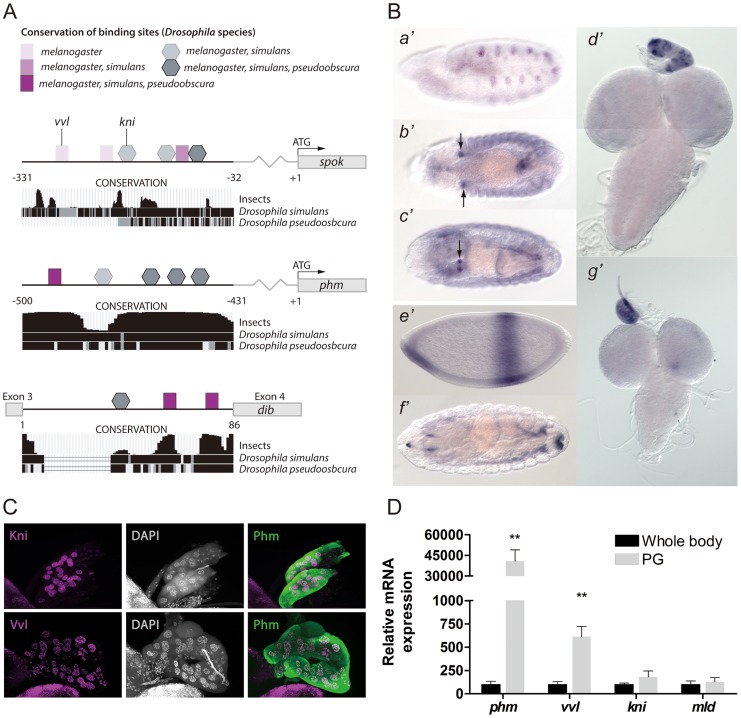
Figure 1. Vvl and Kni have binding sites in the promoters and enhancers of the ecdysone biosynthetic genes and are expressed in the PG.
(A) An illustration showing binding sites in the PG specific cis-regulatory elements of spok and phm and dib. Binding sites are indicated by squares (Vvl) and pentagons (Kni) with shades indicating the conservation of the site between Drosophila species. Conservation tracks were obtained from the UCSC genome browser. (B) In situ hybridization of embryos and third instar larval brains and ring glands with antisense probes for vvl (a′–d′) or kni (e′–g′). (a′) Stage 11, shows vvl expression in the primordial cells of the trachea, while (b′) stage 13, (c′) stage 16 and (d′) L3 show strong vvl expression in the PG cells of the ring gland. (e′) stage 4, (f′) stage 16 and (g′) L3 show kni expression in the PG of L3 larvae, but not clearly in embryos. (C) Immunostaining of the PG from L3 larvae with antibodies against Kni and Vvl (magenta) and Phm (green). Co-localization with nuclei staining (DAPI: gray) indicates that Vvl and Kni are expressed in the nucleus of the PG cells. (D) Expression of phm, vvl, kni and mld measured by qPCR in tissue from whole body L3 larvae or dissected ring glands containing the PG of L3 larvae (n = 4). vvl is highly expressed in the ring gland compared to whole body, like phm, while the expression of kni and mld show a minor enrichment in the gland. Error bars indicate s.e.m. **P<0.01, versus whole body.