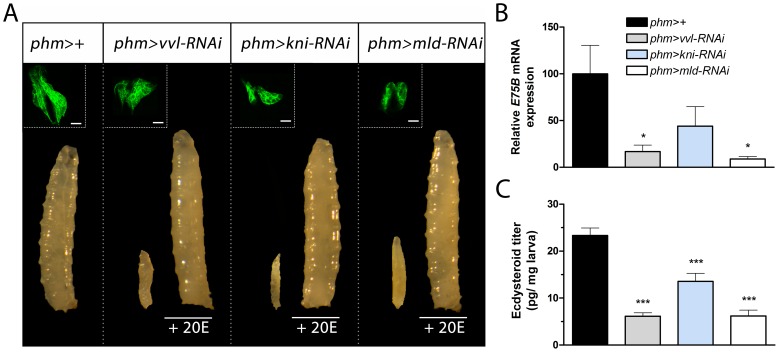
Figure 2. Knock down of vvl, kni and mld in the PG results in developmental arrest and reduces ecdysteroid levels.
(A) RNAi mediated knock down of vvl, kni or mld in the PG using a PG specific driver (phm>) results in developmental L1 arrest for phm>vvl-RNAi and phm>mld-RNAi and L1 and L2 arrest for phm>kni-RNAi larvae. The morphology of the cells in the PG (GFP; green in the top left corner) is normal in phm>GFP,vvl-RNAi, phm>GFP,kni-RNAi and phm>GFP,mld-RNAi animals 36 hours AEL (scale bars, 20 µm). Supplying phm>vvl-RNAi, phm>kni-RNAi and phm>mld-RNAi larvae with 20-hydroxyecdysone (20E) rescues the developmental arrest. (B) Ecdysone levels, as measured by the ecdysone inducible gene E75B, is reduced in the mid-first instar (36 hours AEL) by knock down of vvl, kni or mld in the PG. (C) Ecdysteroid levels measured by ELISA confirm that L1 larvae with reduced expression of vvl, kni or mld in the PG have low levels of ecdysteroids 36 hours AEL compared to the control. Error bars indicate s.e.m. (n = 4). *P<0.05, ***P<0.001, versus the phm>+ control.