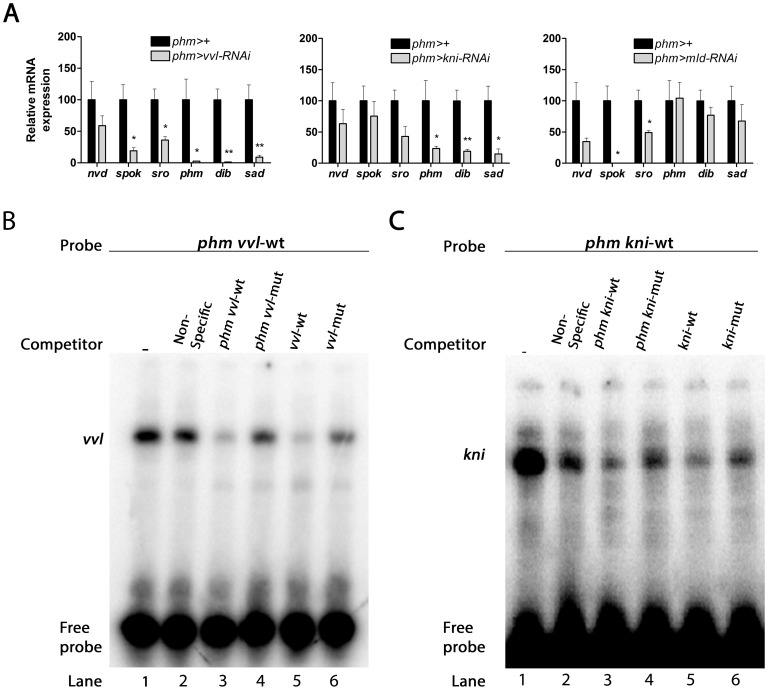
Figure 3. vvl, kni and mld are required for the expression of genes in the ecdysone biosynthetic pathway.
(A) Knock down of vvl, kni and mld in the PG reduces expression of genes in the steroidogenic pathway. vvl knock down results in a down-regulation of spok and sro, catalyzing early steps in the pathway, as well as a reduction of phm, dib and sad mediating the last three steps in the biosynthetic pathway. Knock down of kni results in down-regulation of phm, dib and sad, while knock down of mld causes a specific down-regulation of spok and a moderate reduction of sro. Expression was measured in mid-first instar larvae 36 hours AEL. Error bars indicate s.e.m. (n = 4). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, versus the phm>+ control. (B, C) Direct binding of Vvl or Kni to the regulatory sites in phm promoter indicated by electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA). Nuclear extract was incubated with [γ32]ATP-labeled oligonucleotide sequences of phm promoter containing the vvl (B) or the kni sites (C) and resulted in shifted DNA-protein bands (lane 1). Competition assays were performed with unlabeled non-specific random oligonucleotide sequences (lane 2), the phm promoter containing the vvl or kni sites (lane 3), the phm promoter with mutated vvl or kni sites (lane 4), an oligonucleotide sequence with vvl or kni consensus motif sequence (lane 5), or with the consensus motif mutated (lane 6).