Figure 4.
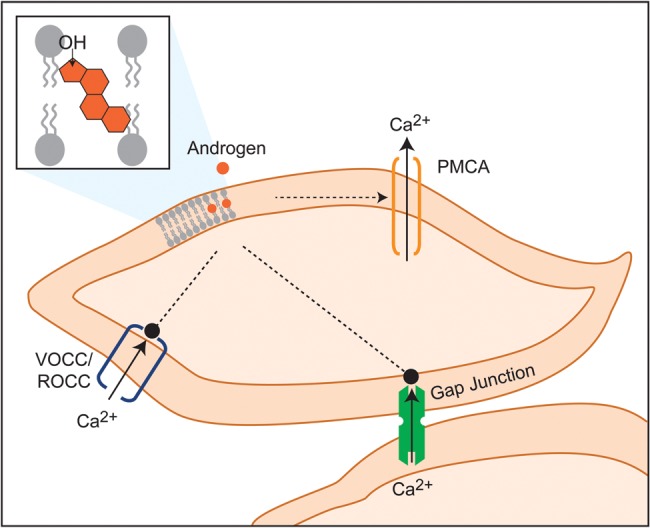
Hypothetical targets of androgens in modulation of MSMC relaxation. Androgens are hypothesized to interact with contractile machinery of MSMCs via penetration into the lipid bilayer. This might promote PMCA to induce rapid Ca2+ efflux, block VOCCs and ROCCs and impair IGJC via effects on the gap junctions. PMCA, Ca2+ ATPase; VOCC, voltage-operated Ca2+ channels; ROCC, receptor-operated Ca2+ channels; IGJC, intercellular gap junctional communication.
