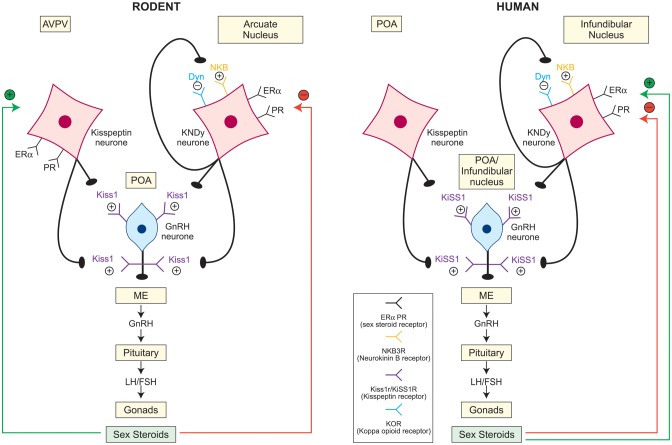
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram showing the neuroanatomy of the kisspeptin-GnRH pathway and the relationship between KNDy neurones and GnRH neurones in humans and rodents. Kisspeptin signals directly to the GnRH neurones, which express kisspeptin receptor. The location of kisspeptin neurone populations within the hypothalamus is species specific, residing within the anteroventral periventricular nucleus (AVPV) and the arcuate nucleus in rodents, and within the preoptic area (POA) and the infundibular nucleus in humans. Kisspeptin neurones in the infundibular (humans)/arcuate (rodents) nucleus co-express neurokinin B and dynorphin (KNDy neurones), which via neurokinin B receptor and kappa opioid peptide receptor autosynaptically regulate pulsatile kisspeptin secretion, with neurokinin B being stimulatory and dynorphin inhibitory. Negative (red) and positive (green) sex steroid feedback is mediated via distinct kisspeptin populations in rodents, via the AVPV and the arcuate nucleus, respectively. In humans KNDy neurones in the infundibular nucleus relay both negative (red) and positive (green) feedback. The role of the POA kisspeptin population in mediating sex steroid feedback in humans is incompletely explored. ME, median eminence; +, stimulatory; −, inhibitory; ERα, estrogen receptor alpha; PR, progesterone receptor; Kiss1/KiSS1, kisspeptin; NKB, neurokinin B; Dyn, dynorphin.