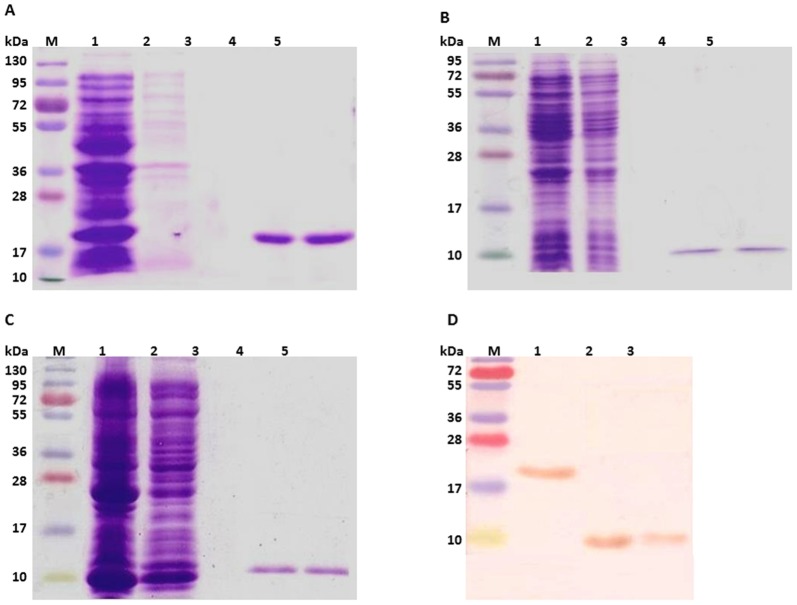
Figure 1. Purification and immune-localization of recombinant Wol GreA and its N and C-terminal domains.
(A) Purification of Wol GreA from Rosetta strain of E. coli by affinity chromatography. Lane M, protein marker; Lane 1, soluble E. coli proteins following induction with 0.5-mM IPTG at 25°C for 6 h; Lane 2, flow through; Lane 3, washed fraction; Lanes 4-5, eluted fractions of His-tagged purified recombinant Wol GreA at 250-mM imidazole conc. (B) Purification of Wol NTD from E. coli expression host, Rosetta by Ni-NTA column. Lane M, protein marker; Lane 1, soluble E. coli proteins induced with 0.5-mM IPTG at 25°C for 6 h; Lane 2, flow through; Lane 3, washed fraction; Lanes 4–5, elution of recombinant Wol NTD at 250-mM conc. of imidazole. (C) Wol CTD purified from Rosetta strain of E. coli. Lane M, protein marker; Lane 1, soluble E. coli proteins induced under similar conditions as mentioned for Wol GreA; Lane 2, flow through; Lane 3, washed fraction; Lanes 4–5, eluted fractions of purified recombinant Wol CTD. (D) Immune-localization of recombinant Wol GreA and its domains by anti-His monoclonal antibody in Western blot. Lane M, protein marker; Lane 1, ∼18.7-kDa Wol GreA; Lane 2, ∼9-kDa Wol NTD; Lane 3, ∼10.3-kDa Wol CTD.