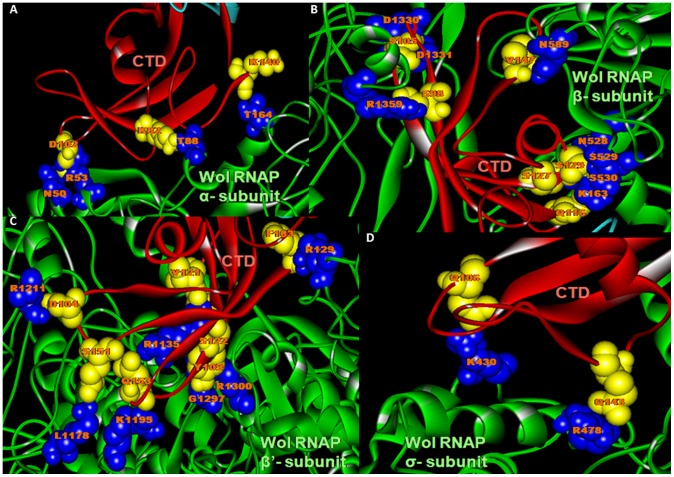
Figure 10. Determination of residual interaction between Wol GreA and α2ββ′σ subunits of Wol RNAP.
(A) The protein docking study between α-subunit of RNAP and Wol GreA exhibited that CTD Lys140 donor atoms involved in hydrogen (H) bonding with acceptor atoms of Wol α subunit Thr164 and Wol CTD Asp120, Lys82 acceptor atoms form H bonding with Wol α subunit donor atoms, Asn50, Arg53, and Thr88. (B) The protein docking between β-subunit of RNAP and Wol GreA exhibited that CTD Ser105, Ser127, Ser129 donor atoms formed H bonding with Wol RNAP β subunit Asn528, Ser529, Asp 1330, Asp1331 acceptor atoms and Wol CTD Ser98, Glu116, Ser129, Val147 acceptor atoms created H bonding by interacting with Wol RNAP β subunit Lys163, Asn528, Ser529, Ser530, Asn589, and Arg1359 donor atoms. (C) Similar to α and β-subunits of RNAP, β′ also solely forms H bonding with CTD residues of Wol GreA where Ser151 donor atom formed H bond with Leu1178 acceptor atom of Wol RNAP β′ subunit and its acceptor atoms Asp104, Tyr109, Val121, Ser122, Glu153, and Phe163 involved in binding with donor atoms of Wol RNAP β′ subunit Arg129, Arg1135, Lys1195, Arg1211, Gly1297, and Arg1300. (D) The protein docking between σ-subunit of RNAP and Wol GreA exhibited that CTD acceptor atoms Glu106, Glu143 created H bonding by interacting with Lys430, Arg478 donor atoms of RNAP σ subunit.