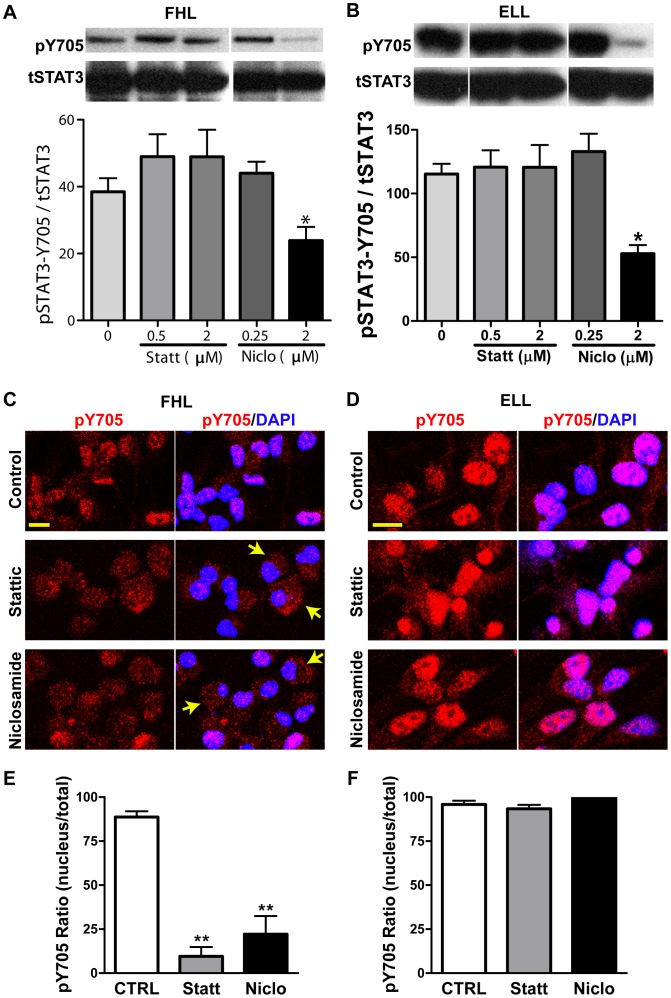
Figure 4. STAT3 phosphorylation in hNSCs treated with STAT3 inhibitors.
(A–B): Western blot analyses of pSTAT3-Tyr705 (pY705) and total STAT3 (tSTAT3) in FHL- or ELL-primed hNSCs, with or without treatment of Stattic and Niclosamide for 24 hrs. GAPDH was used as loading control. Densitometric analysis was performed and normalized values of pSTAT3-Y705/tSTAT3 calculated from 3 independent experiments are graphically represented (Mean ± SEM). In general, FHL-primed hNSCs exhibit a much lower level of pY705 (A) than that in ELL-primed cells (B). STAT3 inhibitors, Stattic and Niclosamide at the doses showing no cytotoxicity, do not affect the phosphorylation of STAT3 at Y705 (pY705); whereas the cytotoxic dose of niclosamide resulted in a significant reduction of pY705 (n = 3, *p<0.05 by One-way ANOVA plus Tukey post-hoc tests). (C–D) Representative confocal images show the immunofluorescent staining of pY705 in hNSCs. Blue are nuclei counterstained with DAPI. pY705 (red) is localized mainly in nuclei of the FHL- or ELL-primed cells without STAT3 inhibitor treatment (Controls in C or D, respectively). Treatment with Stattic (0.5 µM) or Niclosamide (0.25 µM) decreases the nuclear translocation of activated STAT3 (pY705) in FHL- primed hNSCs (C), but not in ELL-primed cells (D). Scale bar, 10 µm. (E–F) Quantitative localization of pY705 STAT3 immunereactivity in the nucleus vs. in a whole cell. **p<0.01. One-way ANOVA with Dunnett post hoc tests. hNSCs: human neural stem cells; ELL: EGF plus LIF and laminin; FHL: FGF2 plus heparin and laminin; Statt: Stattic; Niclo: Niclosamide.