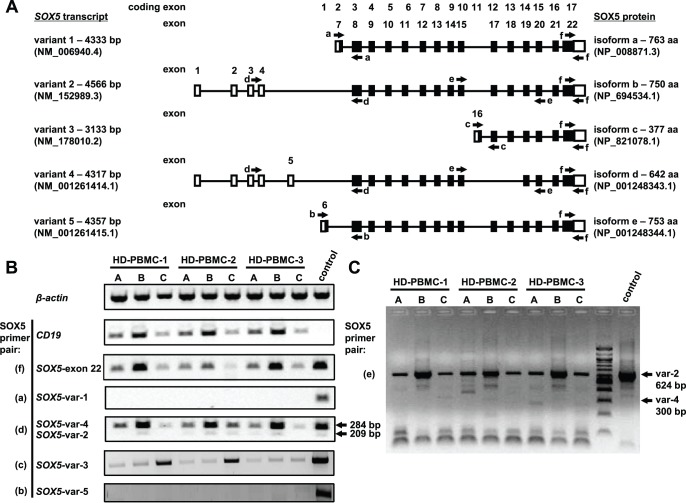
Figure 1. Expression of SOX5 transcript variants in human B cells.
(A) Schematic representation of human SOX5 transcript variants. Non-coding exons are depicted as open rectangles, partial coding exons - as half open rectangles and coding exons - as filled rectangles. Primer regions are indicated with appropriate arrows. Exons and coding exons are numbered according to their location along the genomic sequence, which are drawn as black lines. (B) RT-PCR analysis for the expression of β-actin, CD19 genes and SOX5 transcript variants. HD PBMCs were separated into: A – PBMCs; B – B cells and C – non-B lymphocytes. Except for SOX5 transcript variant 3 (SOX5-var 3) in which human testis RNA sample served as a control, human costal cartilage cells used as a positive control in all RT-PCR reactions. In agarose gel pictures DNA markers were cut out, since they were loaded between the tested samples and the control sample. (C) RT-PCR assay performed to discriminate between SOX5 transcript variant 2 and variant 4 in samples of peripheral blood lymphocytes: A – PBMCs; B – B cells and C – non-B lymphocytes.