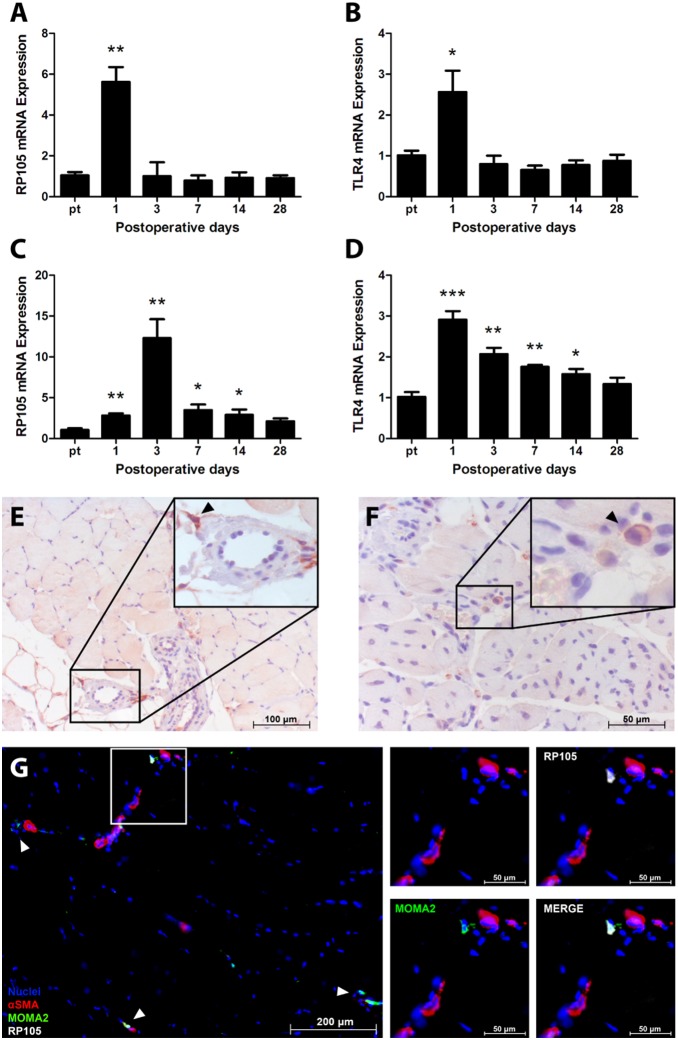
Figure 1. RP105 and TLR4 in arteriogenesis in WT mice.
RP105 mRNA (A) and TLR4 mRNA (B) expression in the adductor muscle group after induction of HLI, measured by real-time quantitative PCR. RP105 mRNA (C) and TLR4 mRNA (D) expression in the ischemic gastrocnemius muscle after induction of HLI, measured by real-time quantitative PCR (n = 4 mice per time point). Expression levels were normalized against either GAPDH or RPL13A. pt = pre-treatment. All values are presented as the mean ± SEM. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, calculated against pre-treatment. Immunohistochemical staining on paraffin-embedded WT adductor muscle group (E) and gastrocnemius muscle (F) 1 day after induction of HLI, using anti-RP105 antibodies. Black arrowheads denote RP105+ cells. (G) Immunohistochemical staining on fresh-frozen sections of WT adductor muscle 1 day after induction of HLI, using anti-αSMA (red), anti-RP105 (white) and anti-MOMA-2 (green) antibodies. Cell nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). White arrowheads denote RP105+MOMA-2+ cells.