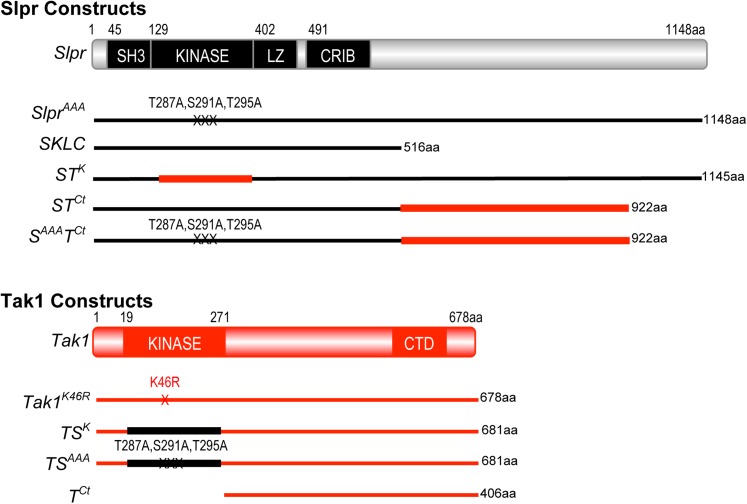
Figure 1.
Slpr and Tak1 domain organization and derived mutant or chimeric constructs. Black lines represent Slpr sequences and red lines indicate Tak1 sequences. The number of amino acids encoded by each construct, minus the epitope tag is given. Slpr encodes four recognizable domains: Src-homology 3 (SH3), kinase, leucine zipper (LZ), and Cdc42/Rac interactive binding motif (CRIB), clustered in the N-terminal half of the protein. Tak1 encodes a protein with an N-terminal kinase domain and a conserved C-terminal domain (CTD) as shown. Specific amino acid point mutations are indicated with an “X.”