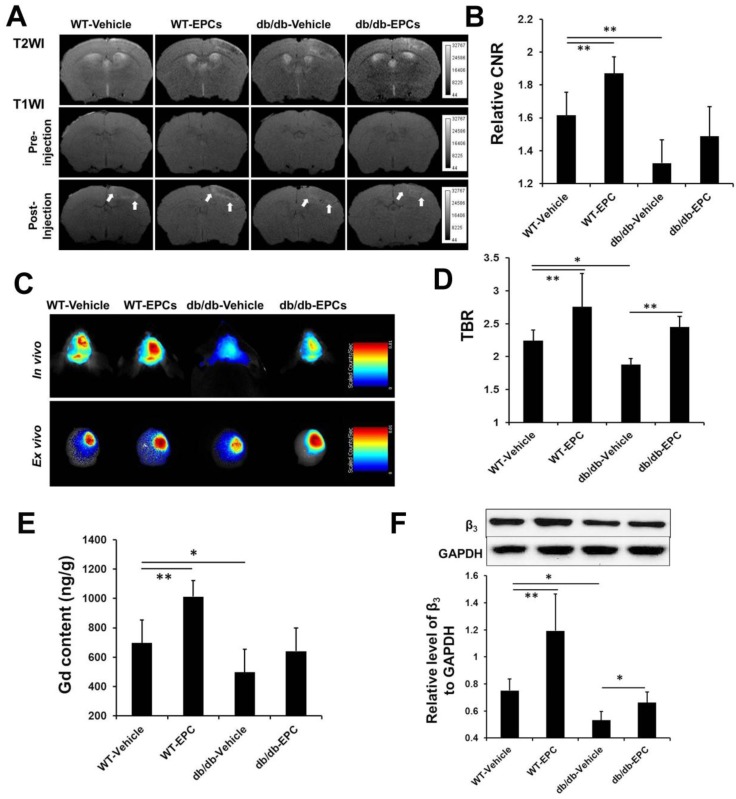
Figure 5.
MRI and NIRF imaging and histological analysis of EPC therapy in ischemic stroke mice. (A) Representative MR images of diabetic and WT mice infused with EPC or saline. (B) The contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) in the WT mice treated with EPC was significantly higher compared with the mice treated with saline. In the diabetic mice, EPC treatment also caused a moderate increase of the CNR on the T1-weighted images (n=6). (C, D) With respect to NIRF imaging, EPC therapy was caused a significant increase of the target-to-background ratio (TBR) in both the diabetic and WT mice (n=6). (E) The gadolinium content in the cerebral hemisphere with ischemia was consistent with the signal enhancement detected on the T1-weighted images (n=6). (F) The expressions of β3 integrin in the EPC-treated diabetic and WT mice were significantly higher compared with the saline-treated mice (n=6). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.