Fig. 1.
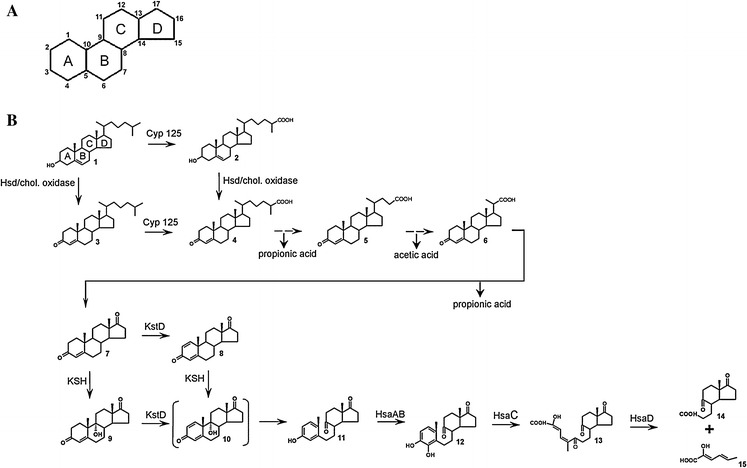
a The basic polycyclic ring structure of sterols and steroids with carbon atoms 1–17. b Proposed cholesterol catabolism in Rhodococcus species and Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Adapted from Van der Geize et al. 2007). Dashed arrows indicate multiple enzymatic steps. The depicted steroids are 1 5-cholestene-3β-ol (cholesterol), 2 5-cholestene-26-oic acid-3β-ol, 3 4-cholestene-3-one, 4 4-cholestene-26oic acid-3-one, 5 4-cholestene-24oic acid-3-one, 6 3-oxo-23,24-bisnorchola-4-ene-22-oic acid, 7 4-androstene-3,17-dione (AD), 8 1,4-androstadiene-3,17-dione (ADD), 9 9α-hydroxy-4-androstene-3,17-dione (9OHAD), 10 9α-hydroxy-1,4-androstadiene-3,17-dione (ADD), 11 3-hydroxy-9,10-secoandrost-1,3,5(10)-triene-9,17-dione (3-HSA), 12 3,4-dihydroxy-9,10-secoandrost-1,3,5(10)-triene-9,17-dione (3,4-DHSA), 13 4,5–9,10-diseco-3-hydroxy-5,9,17-trioxoandrosta-1(10),2-diene-4-oic acid (4,9-DSHA), 14 9,17-dioxo-1,2,3,4,10,19-hexanorandrostan-5-oic acid (DOHNAA), 15 2-hydroxyhexa-2,4-diene-oic acid (HHD). The compound between brackets is chemically unstable. Hsd 3β-hydroxy steroid dehydrogenase, Cyp 125 cytochrome P450 CYP125, KstD 3-ketosteroid dehydrogenase, KSH 3-ketosteroid 9α-hydroxylase, HsaAB 3-hydroxy-9,10-seconandrost-1,3,5(10)-triene-9,17-dione 4-hydroxylase, HsaC 3,4-dihydroxy-9,10-secoandrost-1,3,5(10)-triene-9,17-dione dioxygenase, HsaD 4,5–9,10-diseco-3-hydroxy-5,9,17-trioxoandrosta-1(10),2-diene-4-oic acid hydrolase. The A, B, C and D ring of the steroid polycyclic ring structure are indicated in compound 1 (Petrusma 2011)
