Figure 3. Capillary tube rise of low viscosity liquid27.
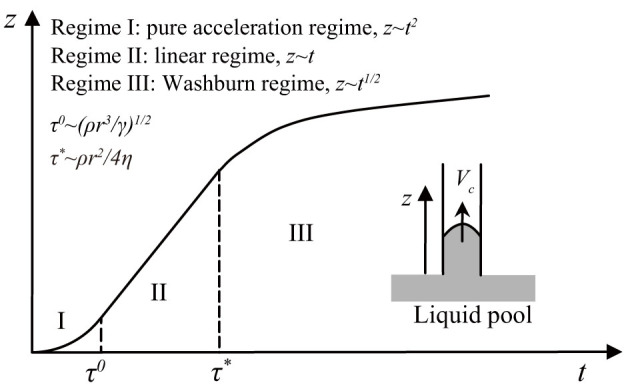
r, z, ρ, γ, η, and Vcare the radius of a capillary tube, height of meniscus, liquid density, surface tension, viscosity, and meniscus rising velocity, respectively. The liquid-air interface of the liquid pool is located at z = 0 and the liquid starts to intrude into the capillary at t = 0. If the liquid is more viscous than gρ3/2r5/2γ−1/2, the capillary tube imbibition process can be divided into three stages28: acceleration, linear, and Washburn regimes (see Supplementary Information for the description of the capillary rise). Accordingly, Σ for a given system can be calculated (Table S5).
