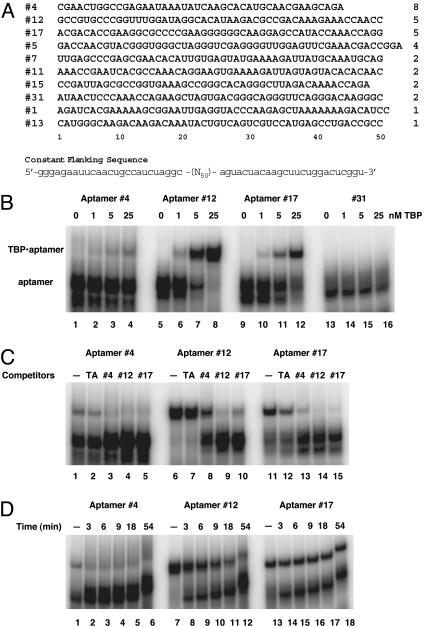
Fig. 1.
Selection and characterization of TBP-aptamers. (A) RNA sequences of the variable region of clones isolated from the 11th generation. The name given each clone is shown to the left of its sequence. The number of isolated individuals is indicated to the right for each clone. The sequence of the flanking constant regions is shown at the bottom. (B) Affinity of TBP-aptamers to yeast TBP. Shown is an EMSA result of 20-μl binding reaction mixture with 0.1 nM radioactive RNA probes and increasing amount of purified His-yTBP. Untagged yTBP was also tested and yielded similar results. (C) TBP-aptamers competing with each other and with TATA-DNA for binding to TBP. Cold competitors (50 nM) were added together with the radioactive probes to reaction mixture containing 25 nM TBP. (D) Stability of the aptamer-TBP complexes. Binding reactions containing 0.1 nM radioactive RNA probes and 25 nM TBP were incubated for 30 min before adding unlabeled RNA to 1 μM final concentration. Aliquots of the mixture were taken out at times indicated and loaded instantly on to a running gel. Lanes labeled with a “minus” sign have no competitor added.