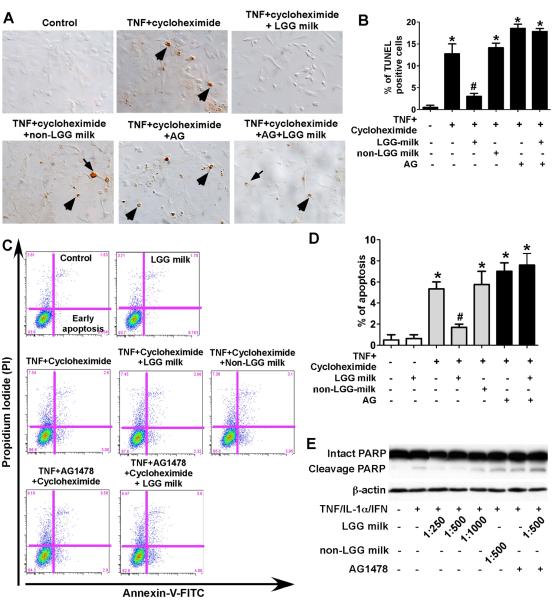
Fig. 3.
LGG milk supernatant inhibits cytokine-induced apoptosis in intestinal epithelial cells. YAMC cells (A–D) were treated with TNF-α (100 ng/ml) and cycloheximide (1 μg/ml) for 6 h in the presence or absence of 1-h pretreatment of supernatants of LGG milk or non-LGG milk at 1:500 dilution, and/or AG1478 (150 nM). The TUNEL assay was performed to detect apoptosis in the YAMC cells. Arrows indicate representative apoptotic nuclei (A). The percentage of cells undergoing apoptosis is shown (B). The YAMC cells were dissociated and stained with Annexin V-FITC and propidium iodide and analyzed by flow cytometry, and results are shown as density plots with Annexin V-FITC vs propidium iodide (C). Viable cells have low Annexin V-FITC and low propidium iodide staining (lower left quadrant); early apoptotic cells have high Annexin V-FITC and low propidium iodide (lower right quadrant); late apoptotic cells have high Annexin V-FITC and high propidium iodide (upper right quadrant); and necrotic cells have low Annexin V-FITC and high propidium iodide staining (upper left quadrant). The early apoptotic cell populations in the lower right quadrant are shown in D. HT-29 cells (E) were treated with the “cytokine cocktail” combination of TNF-α (100 ng/ml), IL-1α (10 ng/ml), and IFN-γ (100 ng/ml) for 12 h in the presence or absence of supernatants of LGG milk or non-LGG milk at indicated dilutions, and/or AG1478 (150 nM). Total cellular lysates were subjected to Western blot analysis using an anti-PARP antibody which indentifies both intact and cleavage PARP. β-actin blot was performed for protein loading control. In B and D, * P < 0.05 compared to control, # P < 0.05 compared to TNF + cycleheximide treated group. The data from Western blot analysis are representative of two separate experiments.