Figure 7.
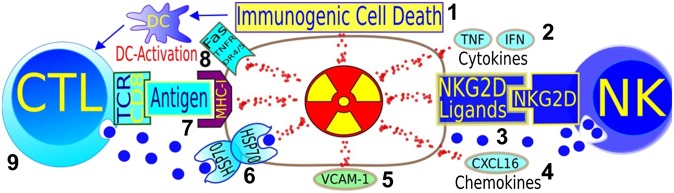
Pathways where radiation can synergize with immune adjuvant therapy for cancer. (1) Immunogenic cell death is promoted by ionizing radiation, through dendritic cell activation and, consequently, T-cell expansion. (2) Cytokines play a role in radiation therapy success. (3) NKG2D-ligands, sensitizing stressed cells to natural killer cells (innate immunity) are upregulated by radiation. (4) Chemokines can be induced by radiation, attracting effector T-cells to the tumour. (5) Radiation-induced interferon-gamma-dependent upregulation of cell adhesion molecule also influences antitumour immunity. (6) Heat shock proteins sensitize to cytotoxic granzymes. (7) Radiation can lead to enhanced expression of major histocompatibility complex (MCH)-I and to de novo expression of neoantigens. (8) Death receptors can be upregulated by irradiation. (9) CD8 T-cells are essential for the success of radiotherapy. Image courtesy of Norman Reppingen, Technical University of Darmstadt, Darmstadt, Germany. CTL, cytotoxic T cell; DC, dendritic cell; IFN, interferon; TCR, T cell receptor; TNF, tumour necrosis factor.
