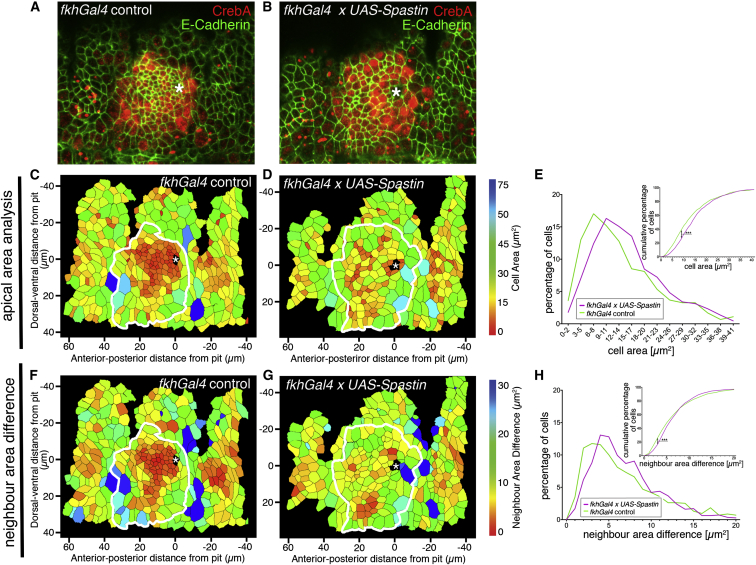
Figure 3.
Depletion of the Microtubule Network Disrupts Apical Area Constriction in the Placode
(A and B) The MT cytoskeleton was depleted using expression of UAS-Spastin under fkhGal4 control. Representative surface view images of control (A) and MT-depleted (B) placodes at late stage 11, with E-cadherin (green) labeling cell outlines and CrebA (red) marking the cells of the placode. Asterisks denote the invagination point.
(C and D) Heat maps corresponding to (A) and (B), respectively, indicating apical surface area size determined through automated tracing of E-cadherin-labeled cell boundaries. White lines denote the border of the placode (determined from CrebA labeling).
(E) Quantification of apical area size in MT-depleted (fkhGal4 x UAS-Spastin) and control (fkhGal4) placodes at late stage 11, showing both the percentage of cells in different-size bins (large graph) and the cumulative percentage of cells relative to apical area size (inset: ∗∗∗p << 0.001 using Kolmogorov-Smirnov two-sample test; see Table S1). Ten placodes were segmented and analyzed for each condition; the total number of cells traced was N(fkhGal4) = 1,198 and N(fkhGal4 x UAS-Spastin) = 1,122.
(F and G) Heat maps corresponding to (A) and (B), respectively, indicating the difference in apical surface area size between any given cell and its direct neighbors.
(H) Quantification of (F) and (G) as for apical area differences above (N(fkhGal4) = 1,148, N(fkhGal4 x UAS-Spastin) = 1,117; inset: ∗∗∗p << 0.001 using Kolmogorov-Smirnov two-sample test; see Table S1).
See also Figure S2.