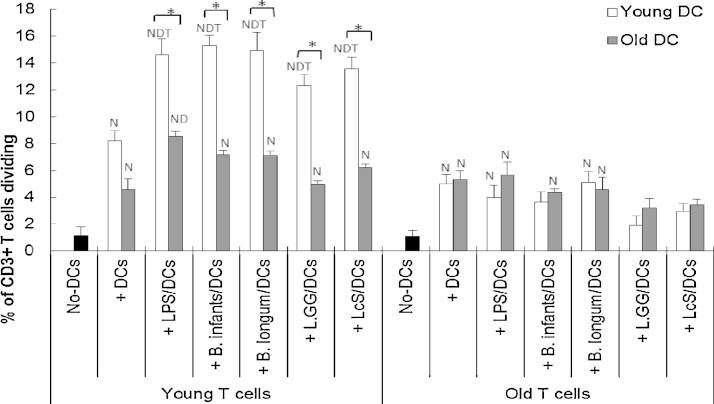
Fig. 8.
Effects of probiotics on proliferation of T cells in the MLR.
T cells in the MLR culture were identified by staining with anti-CD3. Data are presented as % of T cells diving induced by un-stimulated or LPS/probiotics-stimulated DCs. Data are mean ± SE for n = 8 samples from each group. Data were normalised by the Johnson Transformation. There was a significant effect of age (P < 0.01) on T cell proliferation and of treatment (P < 0.01) on young T cell proliferation (two-way ANOVA). Significant differences are denoted as NP < 0.05 relative to no DC control for T cell with the same age group; DP < 0.05 relative to DC incubated T cell (without LPS/probiotics) with the same age group; TP < 0.05 relative to older T cell with the same treatment (post hoc tests with Bonferroni correction).