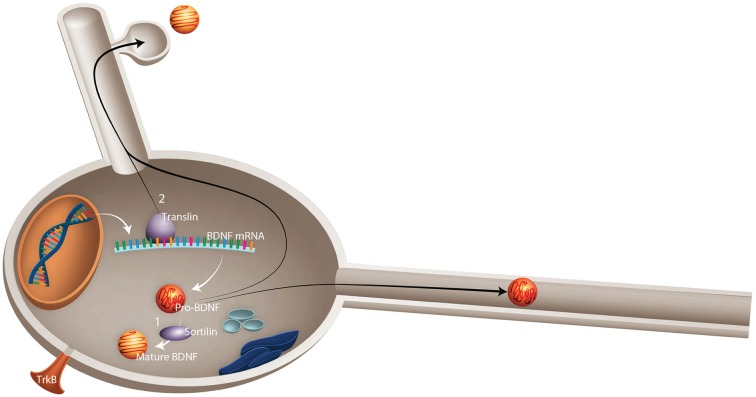
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of possible mechanisms by which val66met substitution in BDNF leads to failed activity-dependent release of BDNF. Val66met substitution alters the dynamics of interaction between BDNF and two important proteins: (1) Sortilin, which is involved in intracellular sorting and pro-neurotrophin signaling. Val66met substitution leads to reduction of BDNF interaction with this protein, which results in mis-sorting into the constitutive secretory pathway instead of activity-dependent release. (2) Translin is a highly conserved protein involved in mRNA transport. An exon found in all BDNF mRNA splice variants contains a specific translin-binding region, which is essential for appropriate BDNF mRNA dendritic targeting. It has been shown that val66met substitution diminishes BDNF mRNA interaction with translin, which leads to reduced translocation of BDNF mRNA to dendrites (Published from Sanchez et al., 2011).