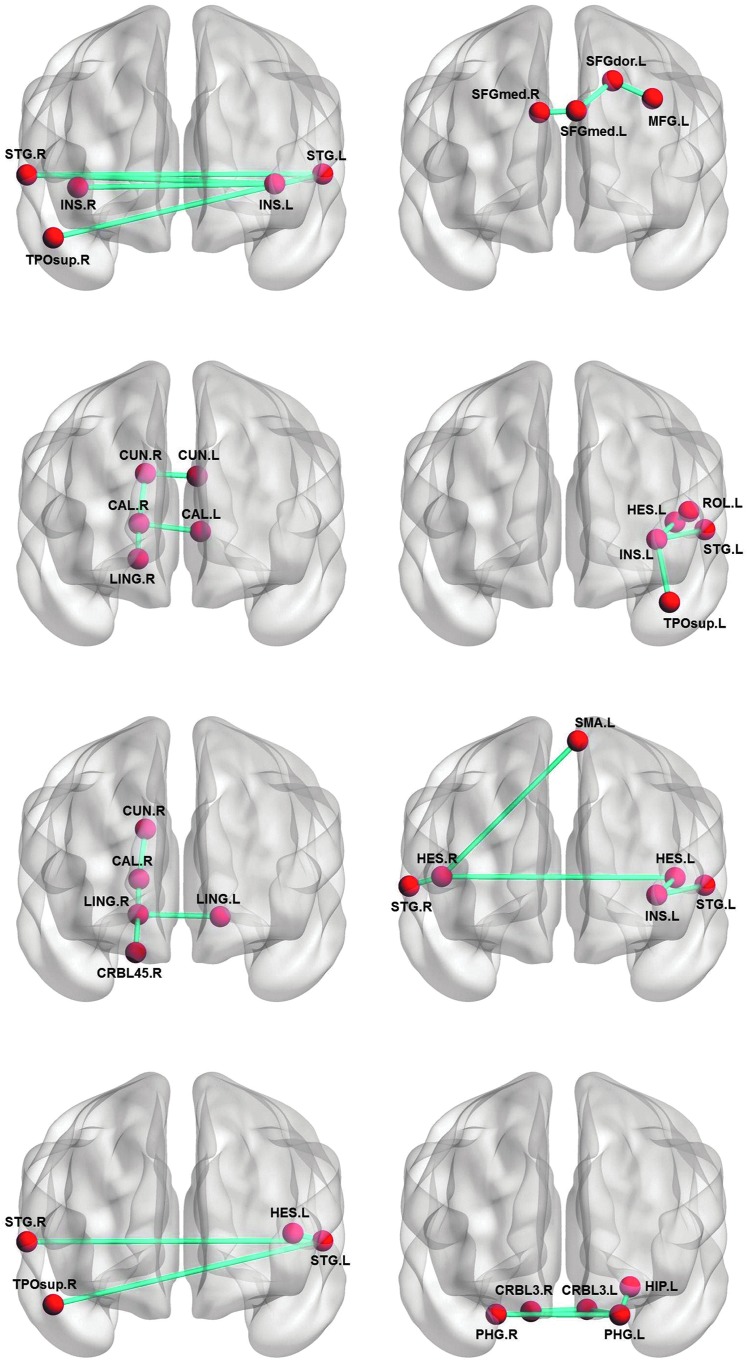
FIG. 4.
The discriminative subnetworks of healthy controls (the left column) and mild cognitive impairment (the right column). INS.L, left insula; INS.R, right insula; STG.L, left superior temporal gyri; STG.R, right superior temporal gyri; TPOsup.R, right superior temporal pole; TPOsup.L, left superior temporal pole; CUN.R, right cuneus; CUN.L, left cuneus; CAL.R, right calcarine sulcus; CAL.L, left calcarine sulcus; LING.R, right lingual gyrus; LING.L, left lingual gyrus; CRBL45.R, right lobule IV, V of cerebellar hemisphere; HES.R, right transverse temporal gyri; HES.L, left transverse temporal gyri; SFGmed.R, right superior frontal gyrus, medial part; SFGmed.L, left superior frontal gyrus, medial part; SFGdor.L, left superior frontal gyrus, dorsolateral; MFG.L, left middle frontal gyrus, lateral part; ROL.L, left rolandic operculum; SMA.L, left supplementary motor area; HIP.L, left hippocampus; PHG.L, left parahippocampal gyrus; PHG.R, right parahippocampal gyrus; CRBL3.L, left Lobule III of cerebellar hemisphere; CRBL.R, right Lobule III of cerebellar hemisphere. Figures were visualized using BrainNet Viewer (www.nitrc.org/projects/bnv/). Color images available online at www.liebertpub.com/brain