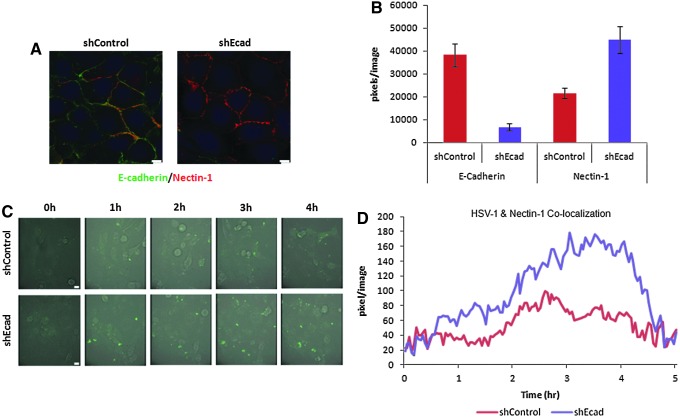
FIG. 4.
HSV-1 colocalization with nectin-1 is enhanced in WRO cells with the EMT phenotype. (A) WRO cells were generated to express Nectin-1-td-tomato, and then transfected with shRNA silencing E-cadherin (WRO-Nectin-1-td-tomato-shEcad), or control (WRO-Nectin-1-td-tomato-shControl). Immunofluorescence microscopy demonstrates nectin-1 (red) and E-cadherin (green) expression in these cells. Scale bars: 10 μm. (B) Image fluorescence quantification shows a reduction of E-cadherin and an increase in nectin-1 expression in WRO-Nectin-1-td-tomato-shEcad as compared with WRO-Nectin-1-td-tomato-shControl. (C) Time-lapse immunofluorescence microscopy shows that HSV-1 VP-16-GFP exhibits earlier and more robust attachment to WRO-Nectin-1-td-tomato-shEcad cells as compared with WRO-Nectin-1-td-tomato-shControl cells. Scale bars: 10 μm. (D) The colocalization of HSV-1 VP-16-GFP (green) with nectin-1 (red) was measured and quantified by Metamorph software analysis of time-lapse immunofluorescence microscopy over a 5-hr period. There is enhanced colocalization of HSV-1 with nectin-1 in the WRO-Nectin-1-td-tomato-shEcad cells as compared with WRO-Nectin-1-td-tomato-shControl cells.