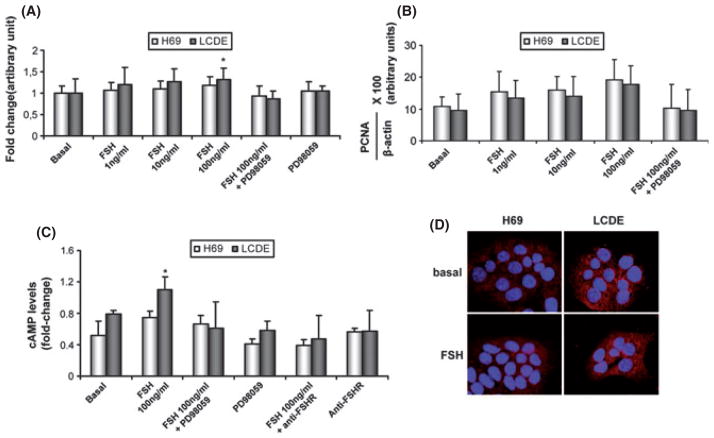
Fig. 6.
Evaluation of cholangiocyte proliferation by MTS assay (A) and by proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) protein expression (B) in H69 (white bar) and in LCDE (black bar) treated with 0.2% BSA (basal) or follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) (1–100 ng/ml with 0.2% BSA) in the absence or presence of PD98059 for 24 h. Intracellular cAMP levels (C) were measured in H69 (white bar) and in LCDE (black bar) treated with 0.2% BSA (basal) or FSH (100 ng/ml with 0.2% BSA) in the absence or presence of PD98059 or an anti-FSHR antibody. FSH significantly increased the growth of LCDE in a dose-dependent manner and the levels of cAMP inside the cell. Effects were blocked by pre-incubation with the inhibitor PD98059 and the anti-FSHR antibody. (D) Immunofluorescence for phospho-extracellular-regulated kinase p-ERK in basal conditions and after treatment with FSH (100 μg/ml) in H69 and LCDE cells. Images show that the hormone increases the phosphorylation of ERK to a higher extent in LCDE cells compared with H69 cultured cells. Data are expressed as mean ± SD of 6 experiments. *P < 0.05 vs. its corresponding basal value.