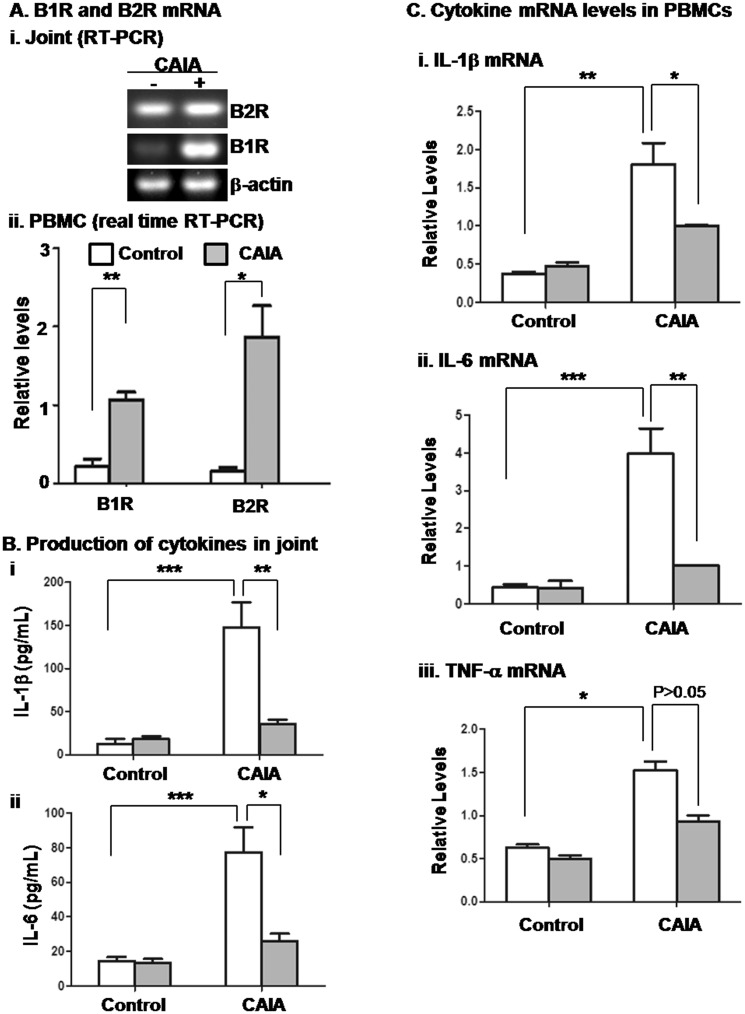
Fig. 2.
B1RB2R deficiency reduces the levels of cytokines in joint tissue and circulating PBMCs
As indicated in the legend for Fig. 1, B1RB2R+/+ and B1RB2R–/– mice received injections of PBS (control) and anti-collagen antibodies plus LPS (CAIA). At the end of the experiments (day 12), the mice were euthanized, followed by removal of the ankle joints and collection of blood. (A) The RNA was purified from (i) joint tissue and (ii) PBMCs of B1RB2R+/+ mice that received injection of PBS (CAIA negative) and anti-collagen antibodies plus LPS (CAIA positive). The mRNA expression of B1R and B2R was evaluated by RT-PCR and real-time RT-PCR, respectively. (B) The levels of (i) IL-1β and (ii) IL-6 in joint tissue were measured using ELISA. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. (C) The cytokine mRNA levels in PBMCs were quantitated by real-time RT-PCR (i–iii). The results were normalized against mRNA of β-actin and relative levels of quantification were calculated. Open column: B1RB2R+/+ mice; filled column: B1RB2R–/– mice. *P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. PBMCs: peripheral blood mononuclear cells; LPS: lipopolysaccharide; CAIA: anti-collagen antibody-induced arthritis.