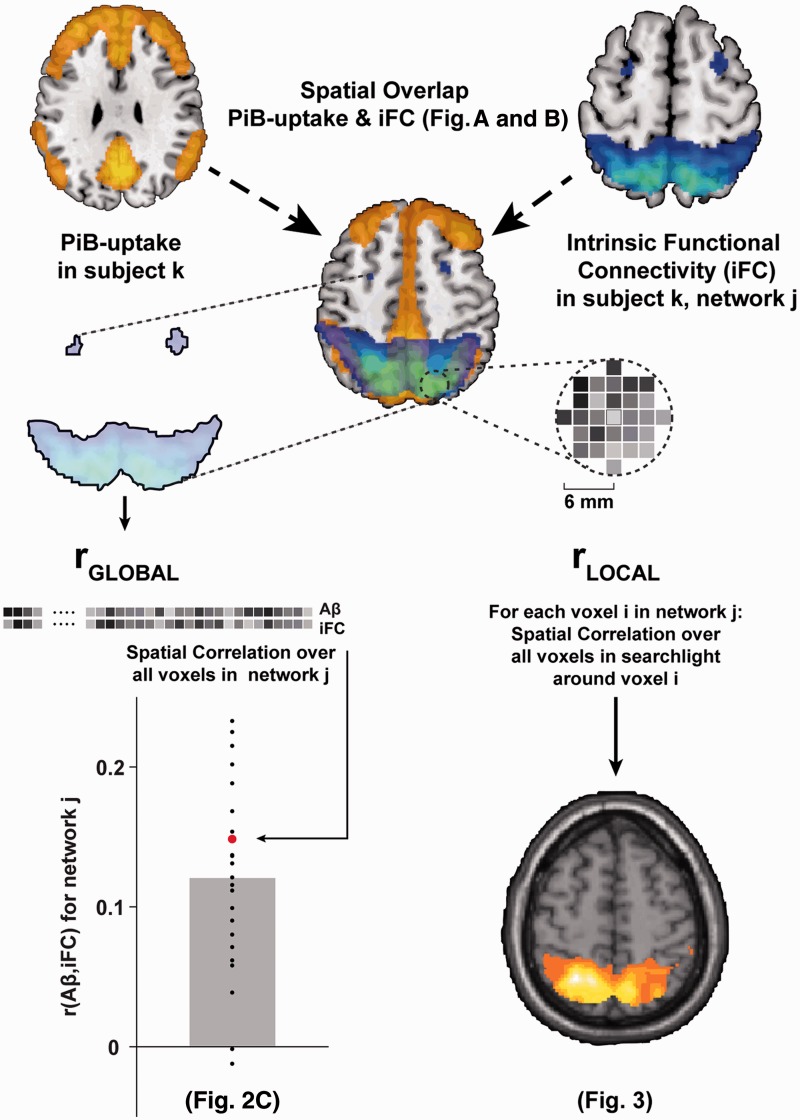
Figure 1.
Overview of analysis approach. For each individual, voxel-wise PiB-uptake was determined as a measure of amyloid plaque density. For each intrinsic network j (as determined by resting-state functional MRI and independent component analysis independent component analysis) in each individual k, we identified the voxels belonging to that network (top right) and extracted the intrinsic functional connectivity (iFC) values of those (∼10 000) voxels. We also extracted that individual’s PiB-uptake values for the same voxels. To determine average plaque load in each network, we then calculated the median PiB-uptake (shown in Fig. 2A and B). We then calculated global and local correlations between both modalities across the entire network and confined to neighbouring voxels. To determine the global spatial correlation between intrinsic functional connectivity and PiB-uptake, we calculated the Pearson correlation coefficient across all selected voxels in the network (rGLOBAL, bottom left and Fig. 2C). After correcting for rGLOBAL (via orthogonalization, see ‘Materials and methods’ section), we then used a searchlight approach to calculate local spatial correlation in the neighborhood surrounding each voxel in the network (rLOCAL, bottom right and Fig. 3). Aβ = amyloid-β.