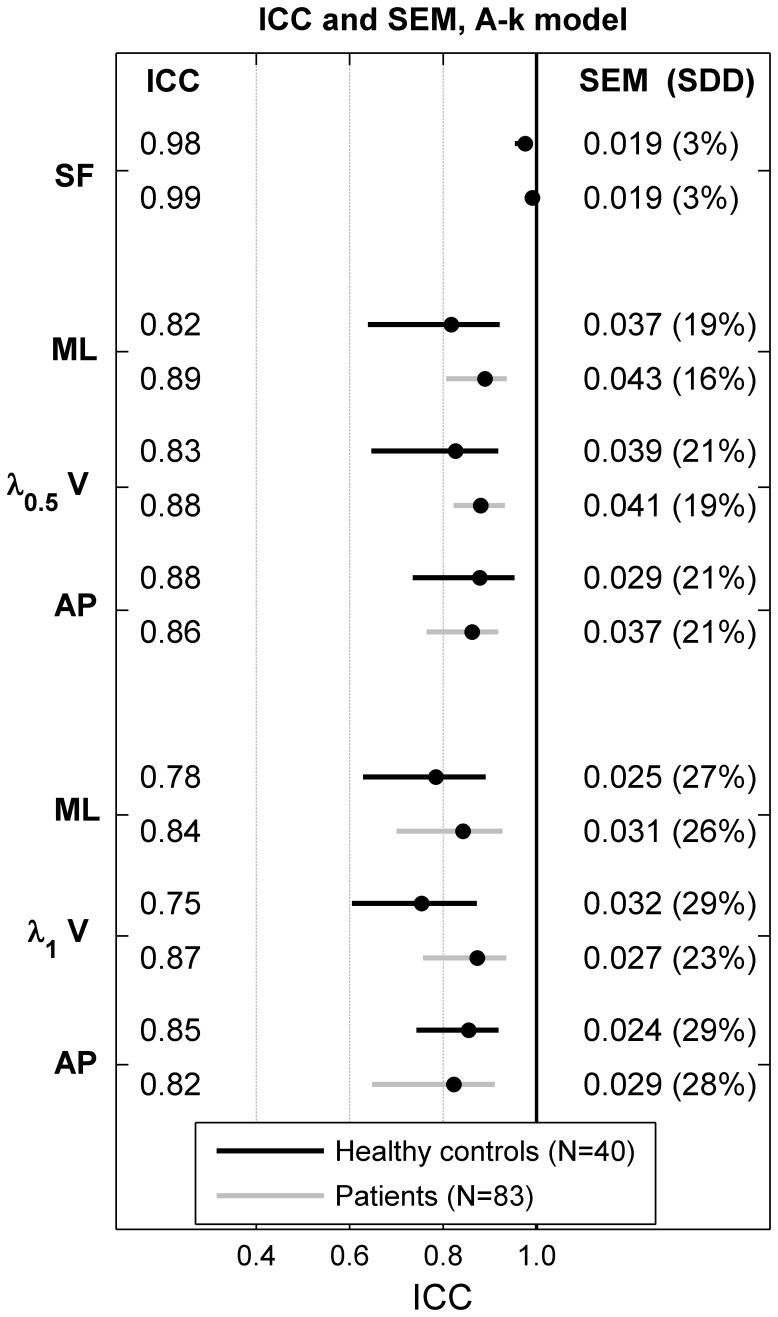
Figure 1. Intrasession reliability of local dynamic stability.
Forty healthy individuals (Healthy controls) and 83 patients exhibiting mild to moderate neurological disorders (Patients) walked 2×30 sec. at preferred speed. A 3D accelerometer recorded the trunk acceleration in medio-lateral (ML), vertical (V) and antero-posterior (AP) directions. The cadence (or step frequency, SF) was assessed by spectral analysis of the vertical acceleration signal. Local dynamic stability was evaluated by computing the rate of the average divergence among nearby trajectories in a reconstructed state-space that reflects the dynamics of locomotion (Lyapunov exponent method). The average divergence was computed either over one step (λ0.5) or over one stride (λ1). The absolute agreement among the two repetitions by intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC(A,k), the standard error of measurement (SEM), and the relative smallest detectable difference (SDD) are shown. The 95% confidence intervals (CI) were computed by bootstrapping (5000 resamples).