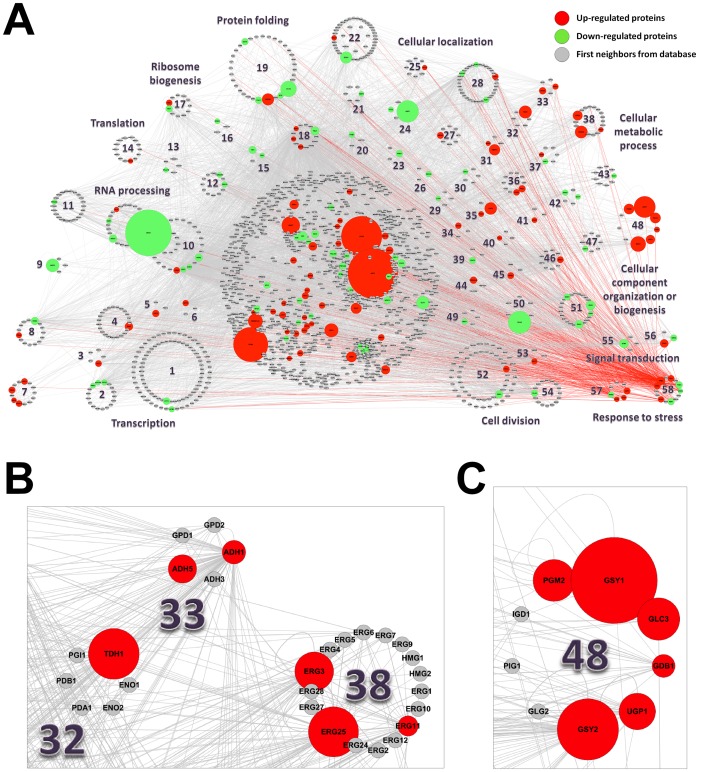
Figure 4. Interactome of S. cerevisiae encapsulated in liquid core alginate-chitosan capsules vs. cells grown freely in suspension, built from proteome data.
(A) The enriched GO biological processes (p≤0.05) among the up-regulated proteins (red), the down-regulated proteins (green) and the background intermediary proteins (grey) from GPMGDID are depicted in the network by clustering the proteins involved in each of the biological processes with a circle layout. Clusters were assigned only to biological processes containing more than three proteins with at least one from the proteome data; proteins belonging to more than one biological process were assigned to clusters with the best enrichment p-values. More specific biological processes are shown only for proteins with more specific annotation in GO database. The nodes sizes of up- and down-regulated proteins are depicted proportional to their fold change (FC ≥1.3, FDR p≤0.05, as described by Westman et al.) [29]. (B) Network zoom showing the glycolysis (GO enrichment p-value of 1.7e-02), NADH oxidation (2.1e-04) and ergosterol biosynthetic process (4.3e-15) clusters. (C) Network zoom showing the glycogen biosynthetic process (2.5e-06) cluster. The network was built using first neighbors expansion, deletion of nodes with degree 0 and 1, addition of different colors and sizes to proteins according to their fold change, and was filtered by Class scores A to C. The network was visualized using Cytoscape v2.8.3 and the proteins were distributed according to selected enriched biological processes (GO) from the “Top Enriched BP” node attribute field by using the group attributes layout. The following enriched biological processes clusters are shown in the network: 1. transcription, DNA-dependent (3.8e-25), 2. chromatin silencing at telomere (6.1e-15), 3. positive regulation of RNA elongation from RNA polymerase II promoter (5.0e-10), 4.positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter (4.2e-19), 5. negative regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent (7.1e-03), 6. positive regulation of transcriptional preinitiation complex assembly (2.5e-05), 7. vacuolar acidification (1.1e-10), 8. replicative cell aging (3.9e-12), 9. pseudohyphal growth (3.6e-08), 10. rRNA processing (4.8e-16), 11. maturation of SSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (1.2e-15), 12. regulation of translation (3.2e-10), 13. regulation of translational fidelity (2.7e-05), 14. mitochondrial translation (9.9e-04), 15. mature ribosome assembly (5.2e-04), 16. ribosomal small subunit assembly and maintenance (1.1e-05), 17. ribosomal large subunit biogenesis and assembly (3.9e-12), 18. protein refolding (1.8e-11), 19. protein folding (7.7e-09), 20. mRNA transport (9.7e-08), 21. poly(A)+ mRNA export from nucleus (5.2e-09), 22. protein transport (1.9e-11), 23. ribosomal small subunit export from nucleus (1.3e-08), 24. protein localization (4.9e-07), 25. protein import into nucleus (6.9e-11), 26. protein targeting to ER (5.2e-04), 27. ER to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport (1.1e-07), 28. endocytosis (9.6e-19), 29. lysine biosynthetic process via aminoadipic acid (7.1e-03), 30. pantothenate biosynthetic process (4.5e-04), 31. heme biosynthetic process (1.3e-03), 32. glycolysis (1.7e-02), 33. NADH oxidation (2.1e-04), 34. phospholipid biosynthetic process (1.1e-02), 35. fatty acid metabolic process (8.9e-04), 36. fatty acid biosynthetic process (2.7e-05), 37. protein amino acid N-linked glycosylation (2.1e-03), 38. ergosterol biosynthetic process (4.3e-15), 39. branched chain family amino acid catabolic process (2.4e-04), 40. pentose-phosphate shunt (2.7e-02), 41. 2-oxoglutarate metabolic process (2.4e-03), 42. one-carbon compound metabolic process (1.2e-02), 43. DNA recombination (5.8e-03), 44. metabolic process (3.0e-03), 45. deoxyribonucleotide biosynthetic process (6.6e-06), 46. protein deubiquitination (1.8e-09), 47. aerobic respiration (3.3e-04), 48. glycogen biosynthetic process (2.5e-06), 49. actin cytoskeleton organization and biogenesis (3.0e-05), 50. actin filament organization (5.1e-12), 51. chitin- and beta-glucan-containing cell wall organization and biogenesis (1.0e-12), 52. cell division (2.8e-21), 53. mitosis (1.5e-17), 54. establishment of cell polarity (2.8e-13), 55. TOR signaling pathway (8.3e-09), 56. Ras protein signal transduction (1.2e-07), 57. response to osmotic stress (1.1e-10), 58. response to stress (3.3e-06).