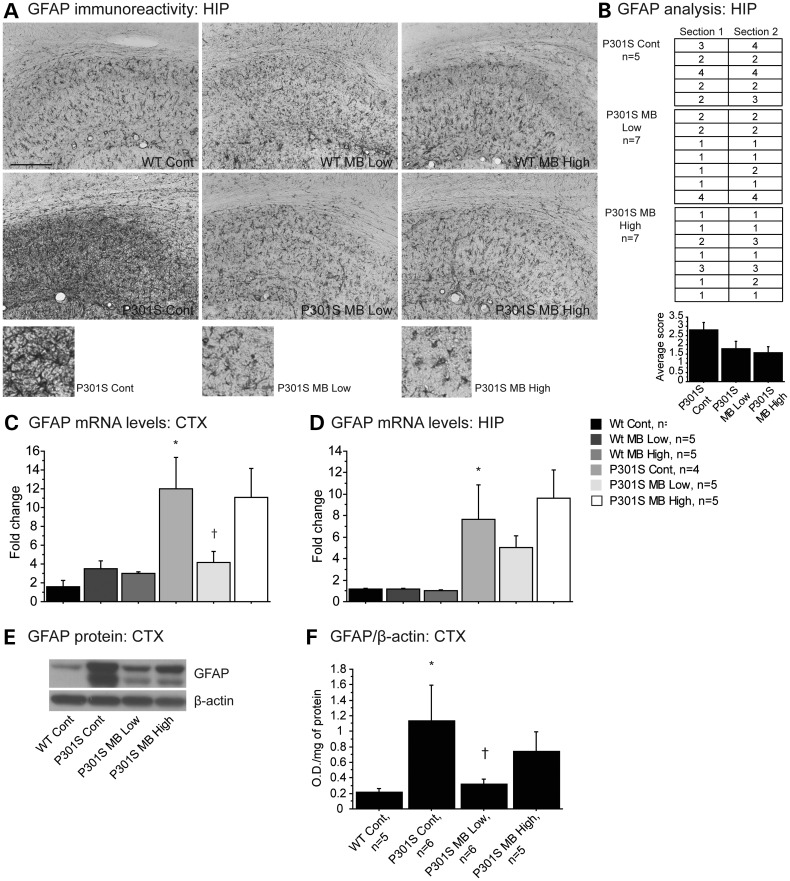
Figure 3.
MB reduced astrogliosis in P301S mice. (A) GFAP immunoreactivity in hippocampus of WT mice fed a control diet (Wt Cont), WT mice fed the MB low dose diet (Wt MB Low), WT mice fed the MB high dose diet (Wt MB High), P301S mice fed a control diet (P301S Cont), P301S mice fed the MB low dose diet (P301S MB Low) and P301S mice fed the MB high dose diet (P301S MB High). (B) Visual analysis of staining in the hippocampus of P301S Cont (n = 5), P301S MB Low (n = 7) and P301S MB High (n = 7). Data expressed as ‘1’ for minimal immunoreactivity, ‘2’ for mild immunoreactivity, ‘3’ for moderate immunoreactivity and ‘4’ for extensive immunoreactivity. MB decreased the apparent levels of GFAP in both P301S mice fed the MB low dose diet and the MB high dose diet when compared with P301S mice fed a control diet. (C) GFAP mRNA levels in cerebral cortex and (D) hippocampus of Wt Cont (n = 4), Wt MB Low (n = 5), Wt MB High (n = 5), P301S Cont (n = 4), P301S MB Low (n = 5) and P301S MB High (n = 5). P301S mice fed a control diet showed significantly increased mRNA levels of GFAP when compared with WT mice fed a control diet. MB significantly decreased GFAP in the cerebral cortex of P301S mice fed the MB low dose when compared with P301S mice fed a control diet (Fisher's PLSD, †P < 0.05). (E) Western blot of GFAP and (F) quantification by optical densities normalized to β-actin. P301S mice fed a control diet showed significantly increased levels of GFAP protein compared with WT mice fed a control diet. Mice fed MB low dose diet showed significantly decreased GFAP protein when compared with P301S mice fed a control diet (Fisher's PLSD, †P < 0.05).