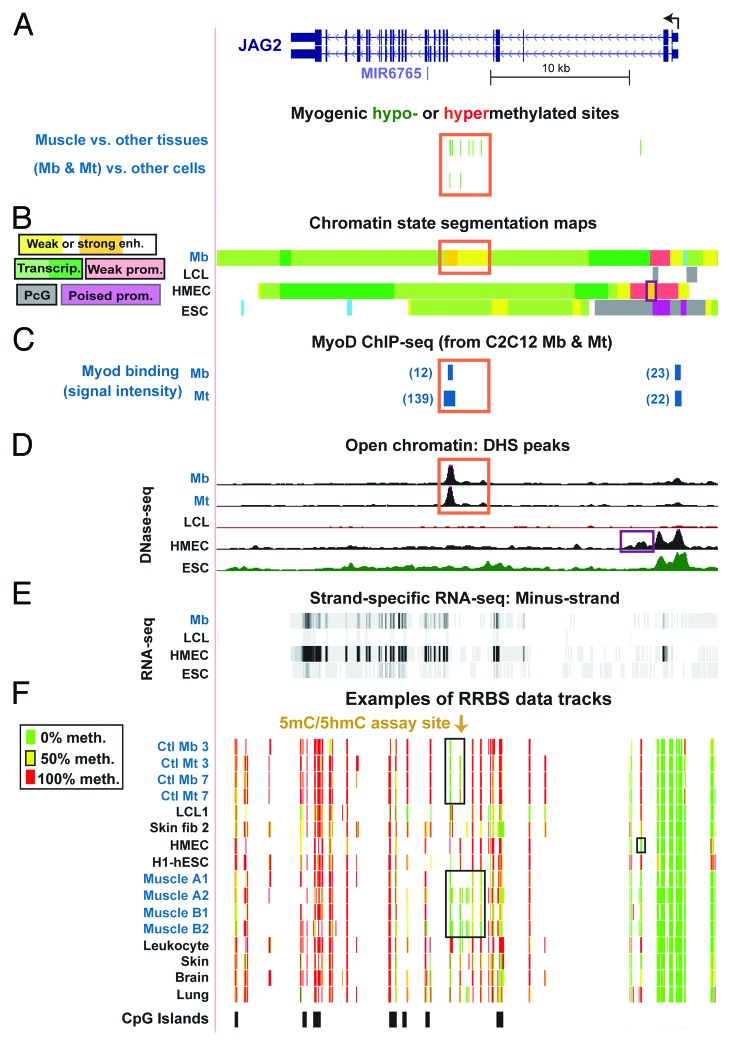
Figure 3. Myogenesis-associated hypomethylation and chromatin epigenetic marks in JAG2 intron 5. (A) Myogenic hypomethylated CpG sites (green, 2 Mb -and-Mt sites and 10 muscle sites) and the absence of hypermethylated sites (red) in JAG2 intron 5. (B) The predicted type of chromatin is shown as in Figure 1B, with the addition of designations for polycomb-type H3K27 trimethylation (PcG), which is usually repressive, and poised promoter (poised prom), which usually contains both H3K27me3 and H3K4me3.57 (C) MyoD binding from C2C12 ChIP-seq29 and identification of orthologous human sequences. The relative binding strength is indicated. Sites shown in blue in this and subsequent figures overlapped variants of the MyoD consensus sequence (CAGCTG, V$MYOD_01, V$MYOD_Q6, or E47 sites from http://genome.ucsc.edu, Conserved TFBS). (D) DNase-seq. (E) RNA-seq data for the minus-strand (http://genome.ucsc.edu; vertical viewing range, 1-to-200). In this region, no specific signal was seen for the plus-strand nor for <200 nt RNA-seq (http://genome.ucsc.edu). (F) Examples of RRBS data tracks as in Figure 1. Orange boxes, overlapping epigenetic features in panels a, b, and c. The chr14:105,601,999–105,638,022 region is shown.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.