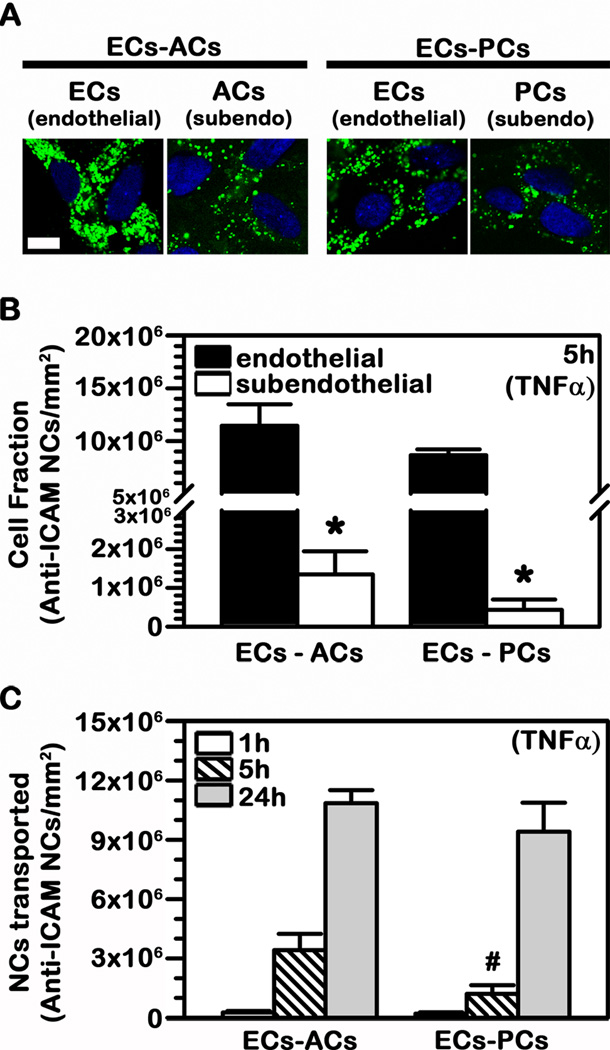
Fig. 7.
Binding and transport of anti-ICAM NCs across BBB cell bilayers. TNFα-activated human brain microvascular endothelial cells (ECs) were grown to confluence on the apical side of porous-membrane transwell inserts while activated astrocytes (ACs) or pericytes (PCs) were grown on the opposing basolateral side of the membrane (subendothelial layer). FITC-labeled or 125I-labeled anti-ICAM NCs were added to the apical chamber above the cells and incubations were carried at 37°C for 1 h, 5 h, or 24 h. (A) Confocal images of anti-ICAM NCs associated to the endothelial and subendothelial cell layers after 24 h incubation. Cell nuclei are stained with blue DAPI. Scale bar = 10 μm. (B) Total 125I-anti-ICAM NCs associated per mm2 of endothelial vs. subendothelial layer after 5 h incubation. (C) Total 125I-anti-ICAM NCs transported per mm2 of endothelial+subendothelial bilayers over time. (B–C) Data are mean ± SEM. *Comparison between the endothelial layer (ECs) and sub-endothelial layer (ACs or PCs); #comparison between the ECs-ACs bilayer and the ECs-PCs bilayer (p<0.05 by Student’s t-test).