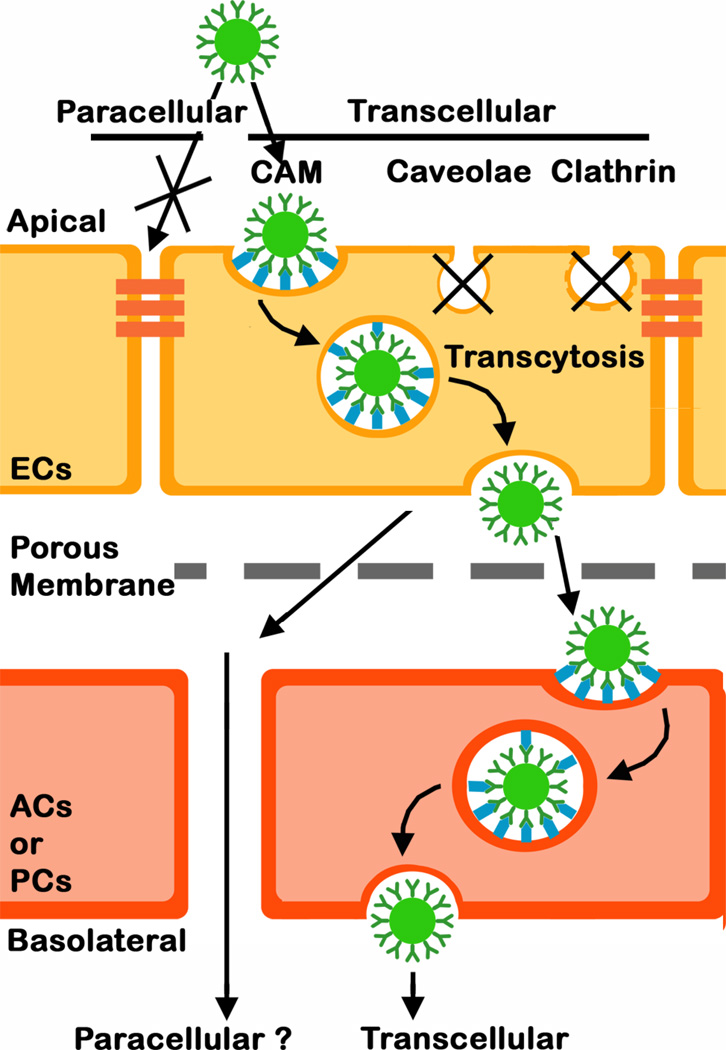
Fig. 8.
Schematic representation of the transport of anti-ICAM NCs across a co-culture model of the BBB. Anti-ICAM NCs bind specifically to ICAM-1 on the apical surface of endothelial cells (ECs) and induce endocytic uptake via the cell adhesion molecule- (CAM)-mediated pathway. This is a clathrin- and caveolae-independent mechanism, which results in transport of anti-ICAM NCs across the cell body via transcytosis (the transcellular route) vs. the paracellular route between adjacent cells. Anti-ICAM NCs are also endocytsed by astrocytes (ACs) and pericytes (PCs) underlining ECs and can traverse this subendothelial layer.