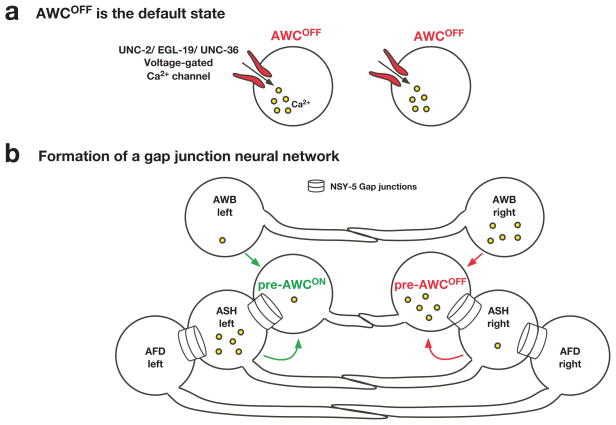
FIG. 2. A transient embryonic gap junction neural network coordinates stochastic AWC asymmetry.
(a) Prior to cell-cell communication, both AWC neurons have high intracellular calcium levels and symmetrically exist in the default AWCOFF state.
(b) AWC, ASH, AFD, and AWB sensory neurons are part of a transient embryonic neural network connected by NSY-5 gap junctions and contribute to the decision making of stochastic AWC asymmetry. Differences in calcium levels between left and right sides of neuronal pairs promote the AWCON or AWCOFF subtype, depending on the cellular context. AWC asymmetry is stochastic, and this figure illustrates the case when AWCON is on the left and AWCOFF is on the right.