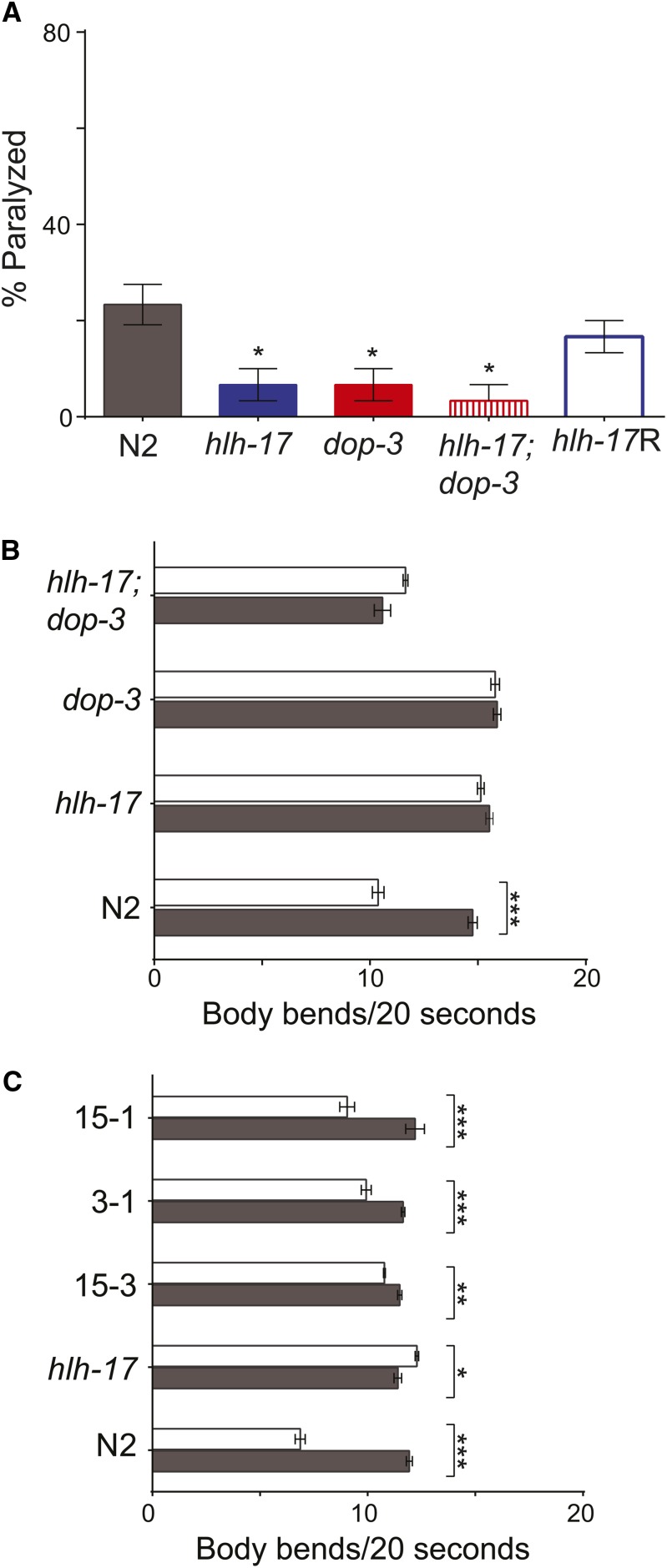
Figure 1.
HLH-17 functions upstream of dop-3 to regulate dopamine signaling. (A) DA-induced paralysis: hlh-17(ns204), dop-3 (vs106), and hlh-17(ns204); dop-3 (vs106) animals are less sensitive than wild-type animals to 10 mM DA. Transgenic expression of HLH-17::GFP in hlh-17(ns204) animals rescues the DA-induced paralysis phenotype. The bar for hlh-17R represents the average measurements from three biological replicas of three independent lines. *Statistical significance when compared to wild-type, n = 10 animals/strain/rep for three biological replicas. (B) Basal slowing response: Well-fed wild-type animals, but not hlh-17(ns204), dop-3 (vs106), or hlh-17(ns204); dop-3 (vs106) animals, move significantly slower in the presence of food (white bars) than in the absence of food (gray bars). (C) Transgenic expression of HLH-17::GFP rescues the basal slowing response of hlh-17(ns204) animals. Three independent lines, 15.3, 15-1, and 3.1, were assayed. In (B) and (C), five animals/rep/strain for a total of three biological replicas were assayed. Each animal was analyzed for three separate 20-sec intervals, so that the total number of observations was 15 observations/rep/strain. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.005; ***P < 0.0005.