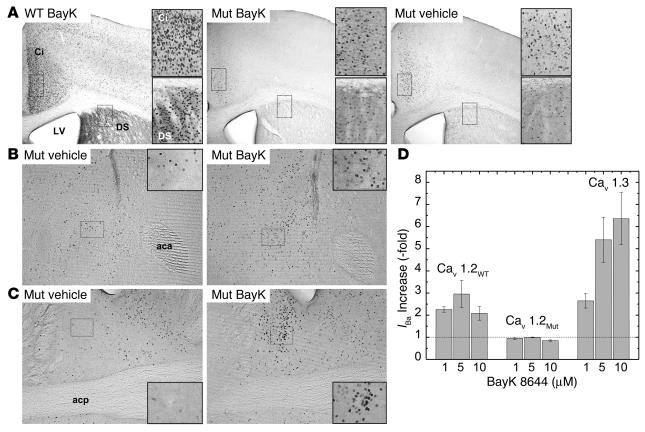
Figure 6.
BayK-induced Fos expression in WT and Cav1.2DHP–/– mice. Mice were injected with vehicle or BayK solution (WT, 2 mg/kg; mutants, 4 mg/kg) and Fos expression was quantified by immunohistochemistry as described in Methods. (A) DS, dorsal striatum; Ci, cingulate cortex; LV, lateral ventricle. Magnification, ∞40. Inset shows higher magnification of boxed areas. (B) Fos expression after BayK (right) or vehicle (left) application in the nucleus accumbens. aca, anterior commissure, anterior. Magnification, ∞100. Inset magnification, ∞800. (C) Fos expression after BayK (right) or vehicle (left) application in the BNST. Magnification, ∞100. Inset magnification, ∞800 (boxed area in the lateral division). acp, anterior commissure, posterior. (D) Stimulation of IBa through Cav1.2 (Cav1.2WT), mutant Cav1.2 (Cav1.2MUT), and Cav1.3 by BayK after heterologous expression under identical conditions in tsA-201 cells as described (15). Based on DHP pharmacokinetic data in mice (53), we calculated BayK concentration in brain to reach concentrations between ∼7 ∝M (peak concentration) and ∼1 ∝M (after three elimination half-lives). All data were significantly different from 1 (control before drug application) (P < 0.05; one-sample Student's t test) except Cav1.2MUT, 1 ∝M and 5 ∝M BayK).