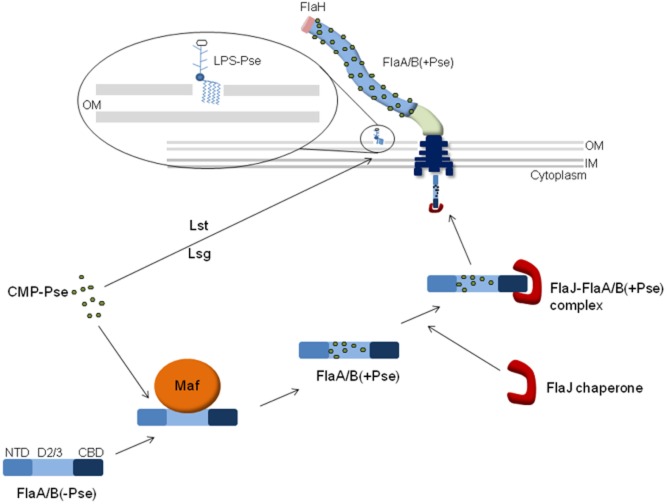
Fig. 6.
Model depicting the flagellin glycosylation and export pathway. Activated pseudaminic acid (CMP-Pse) either is transferred onto a sugar-antigen carrier lipid (ACL) by Lst to create an LPS O-antigen unit, which is subsequently transported across the cytoplasmic membrane by Lsg, or is transferred on to the central D2/3 domain of unglycosylated flagellin the cytoplasm in a Maf dependant manner. Glycosylated flagellin is then bound by the flagellin-specific chaperone FlaJ, which is dependent on presence of C-terminal chaperone-binding domain (CBD) and piloted to the basal body of the flagellar where it is exported via it's dedicated T3SS in an unfolded form. For polymerization, the flagellin is folded, exposing the central D2/3 domain and attached glycans along the surface of the filament. The cytoplasmic glycosylation process occurs independently of the presence of the flagellar cap FlaH and a functional flagellar filament.