Figure 1.
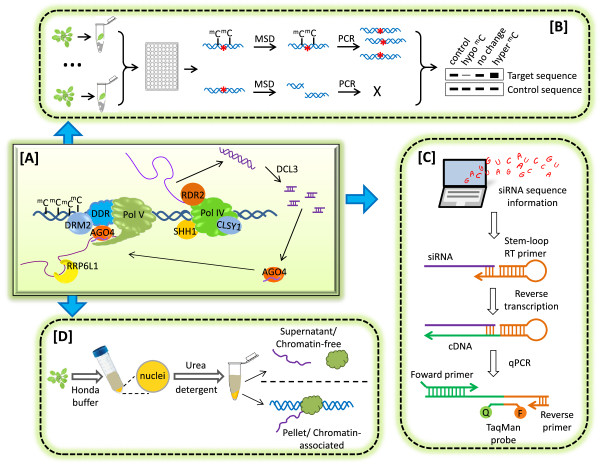
An integrative procedure for studying nucleic acids in RdDM. [A] A model of RdDM in Arabidopsis. Briefly, Pol IV initiates siRNA production by producing single-stranded non-coding RNAs, while Pol V synthesizes scaffold RNAs that recruits Argonaute-associated siRNAs. The complimentary pairing between the two types of non-coding RNAs, as well as physical interactions between proteins in the methylation complex, results in targeting of the methyltransferase DRM2 to RdDM loci. For simplicity, not all known RdDM components are shown. [B] Chop PCR-based screen for mutants showing abnormal DNA methylation patterns. Red asterisks represent enzyme restriction sites. Cytosine methylation overlapping restriction sites will protect DNA from methylation-sensitive digestion (MSD), while enzymatic cleavage results in failure of subsequent PCR amplification of the target sequences. Note that the enzyme McrBc is special in that it cleaves methylated- but not unmethylated DNA sequences (see also Additional file 2: Table S1). [C] RT-qPCR detection of siRNAs by using stem-loop primers during reverse transcription. [D] Schematic procedure of nuclei fractionation, which separates chromatin-associated RNAs from RNAs that are not associated with chromatin. See Methods for details.
