Figure 4.
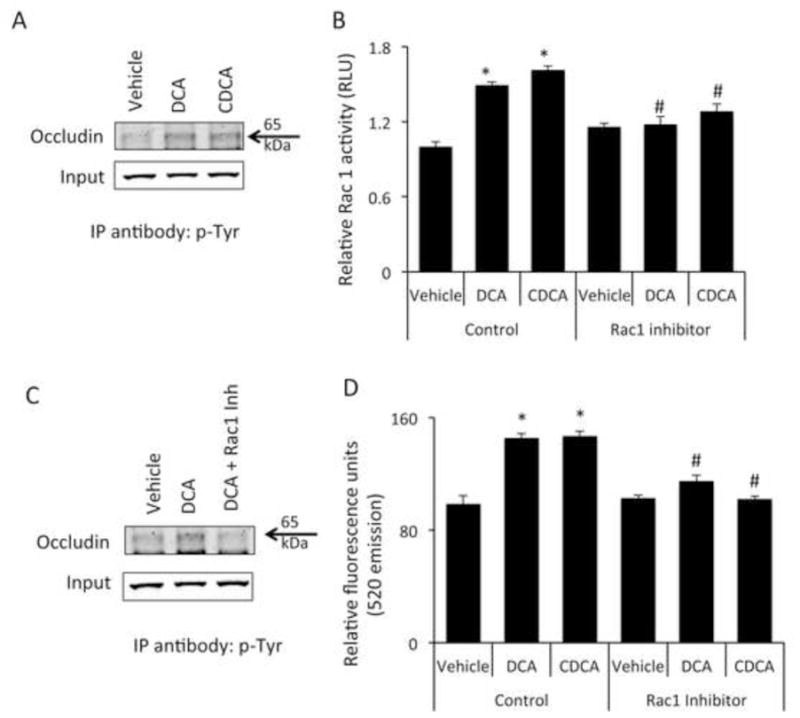
Bile acids increase the phosphorylation of occludin via a Rac1-dependent mechanism (A) Brain microvessel endothelial cells were treated with vehicle, chenodeoxycholic acid or deoxycholic acid for 1 hour and phosphorylated occludin levels were assessed by immunoprecipitating 50μg of total protein with a phospho-tyrosine specific antibody and immunoblotting using and anti-occludin antibody. 10μg total protein lysate was used as input. Cells treated with bile acids show a higher degree of tyrosine phosphorylation of occludin as shown by increased immunoprecipitation with anti-phospho-tyrosine antibody. (B) Confluent monolayers of brain microvessel endothelial cells were treated for 1 hour with vehicle, chenodeoxycholic acid or deoxycholic acid and Rac1 activity was measured. chenodeoxycholic acid or deoxycholic acid induce a significant increase in Rac1 activity compared to vehicle-treated cells, which could be blocked by the pre-treatment with the Rac1 inhibitor NSC23766. (* denotes p<0.05 compared to vehicle; # denotes p<0.05 compared to chenodeoxycholic acid or deoxycholic acid in the absence of NSC23766; n=5). (C) Brain microvessel endothelial cells were treated with vehicle, deoxycholic acid or deoxycholic acid + Rac1 inhibitor (NSC23766) for one hour and phosphorylation of occludin was determined by immunoprecipitating protein lysates with anti-phospho-tyrosine antibody and immunoblotting for occludin. 10μg total protein lysates were loaded for input. Pretreatment with the Rac1 inhibitor NSC23766 inhibited the deoxycholic acid-mediated phosphorylation of occludin. (D) Confluent monolayers of Brain microvessel endothelial cells were treated for 24 hours with vehicle, chenodeoxycholic acid or deoxycholic acid in either the presence or absence of Rac1 inhibitor NSC23766 and fluorescein isothiocyanate-dextran permeability was measured. Pretreatment with NSC23766 inhibited the bile acid-mediated permeabilization of brain endothelial cell monolayers. (* denotes p<0.05 compared to vehicle, # denotes p<0.05 compared to chenodeoxycholic acid or deoxycholic acid in the absence of NSC23766; n=6). (DCA; deoxycholic acid, CDCA; chenodeoxycholic acid; IP immunoprecipitation)
