Figure 5.
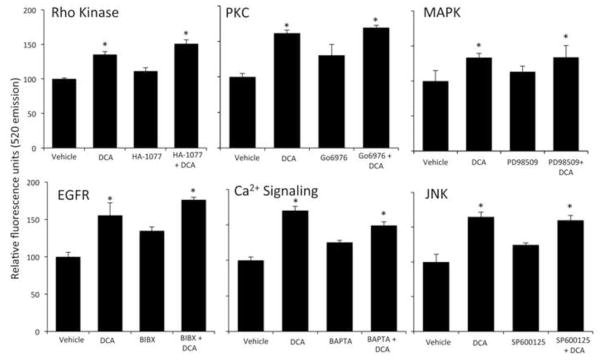
Deoxycholic acid does not disrupt endothelial tight junctions via known signal transduction pathways. Confluent monolayers of brain microvessel endothelial cells were treated for 24 hours with vehicle or deoxycholic acid in either the presence or absence of specific inhibitors for Rho kinase (HA-1077), PKC (Gö6976), ERK1/2 (PD98059), EGFR (BIBX), Ca2+ signaling (BAPTA) or JNK (SP600125), and permeability to fluorescein isothiocyanaate-dextran was measured. Pretreatment with these inhibitors failed to prevent the deoxycholic acid-induced permeability of RBMEC monolayers. (* denotes p<0.05 compared to vehicle, n=6).
