Figure 7.
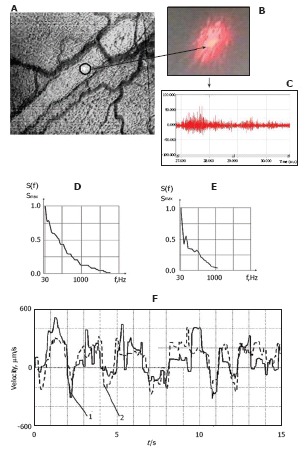
Integration of laser speckle and transmission microscopies for studying lymph flow dynamics. A: A laser beam was focused into a small-diameter spot (~5 μm) on axial lymph flow (microvessel diameter 55 μm); B: Lymph flow randomly modulated the focused Gaussian beam to provide scattered dynamic speckles images; C: Scattered intensity fluctuations were detected by a photodetector and transformed into an electrical output signal. D and E: Spectral shapes from scanning the lymphatic cross-section: (D) the spectrum when the laser beam was focused in axial flow and (E) when the laser beam was focused in flow near the lymphatic wall; F: Real-time dynamics of lymph-flow velocity in a lymph microvessel, recorded with a laser speckle technique (curve 1) and by processing the video recording (curve 2).
