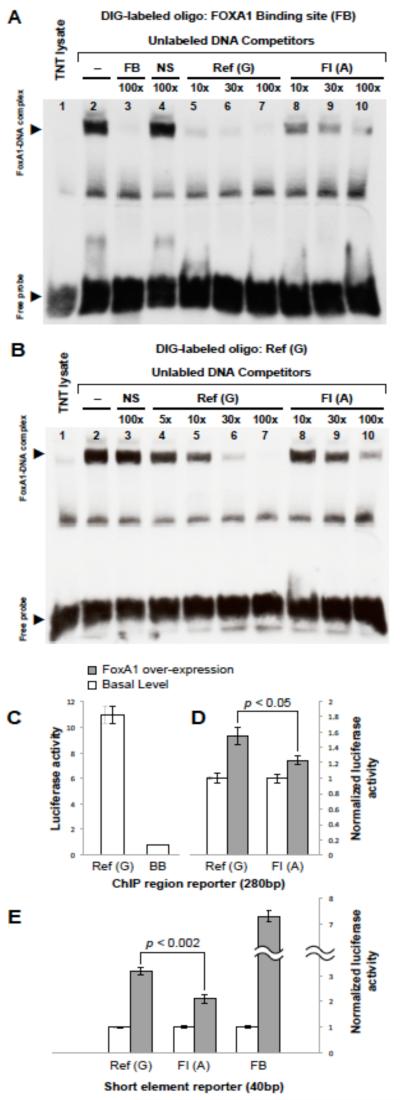
Figure 2.
The FI-associated A allele disrupts FOXA1 binding and transactivation potential at chr11:47227430.
Panels A and B. Gel electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSA) show that FOXA1 binds to the chr11:47227430 site, with the reference G allele having higher affinity for FOXA1 compared to the FI-associated A allele.
(A) A DIG-labeled oligonucleotide containing well-characterized FOXA1 binding site (FB) in the albumin gene enhancer was incubated with unprogrammed reticulocyte lysate (lane 1) or reticulocyte lysate programmed to express FOXA1 (Lanes 2-10). A retarded complex (upper arrowhead) is seen after nondenaturing acrylamide gel electrophoresis (lane 2), which is competed by 100-fold molar excess unlabeled oligonucleotide (lane 3), but not by an equivalent amount of nonspecific competitor oligonucleotide (NS, lane 4). While a synthetic oligonucleotide surrounding the reference G variant can efficiently compete with the DIG-labeled synthetic oligonucleotide carrying the FB site (lanes 5 to 7), the FI-associated A variant cannot displace the labeled probe even when used up to 100-fold molar excess (lanes 8 to 10), suggesting that G->A substitution at the chr11:47227430 site disrupts FOXA1 binding.
(B) Binding and competition assays reciprocal to those in panel A confirm specific binding of FOXA1 to the reference G allele at chr11:47227430. Here, the synthetic oligonucleotide surrounding the reference G allele was labeled with DIG, and is shown to form a specific complex with FOXA1 (lane 2, upper arrowhead) that cannot be efficiently displaced by unlabeled NS oligonucleotide (lane 3). Increasing amounts of an unlabeled oligonucleotide containing the ref-G allele displaces the bound DIG-labeled ref-G oligonucleotide at lower molar fold excess than an unlabeled oligonucleotide carrying the FI-associated A variant (compare lanes 4-7 to lanes 8-10).
Panels C-E. The reference G allele at chr11:47227430 has significantly transactivation potential compared to the FI-associated A allele in luciferase reporter assays.
(C) Dual luciferase assays show that a reporter plasmid containing the 280bp region surrounding the chr11:47227430 site exhibits enhancer activity in HepG2 cells [Ref(G)] compared to the minimal HSV thymidine kinase (TK) promoter in the pGluc Mini-TK backbone (BB).
(D) The 280bp region surrounding chr11:47227430 shows FOXA1-dependent enhancer activity in HepG2 cells. The FI-associated A variant [Ref(A)] is significantly less responsive to FOXA1 over-expression compared to the reference G allele [Ref(G)]. For each construct, luciferase measurements are normalized by the corresponding reporter activity measured in the absence of FOXA1 co-expression.
(E) Luciferase activity was measured for reporter constructs containing 40-mer oligonucleotides centered on the chr11:47227430 reference [Ref(G)] or risk [FI(A)] alleles or a well characterized albumin enhancer FOXA1 binding site (FB). For each construct, luciferase measurements are normalized by the corresponding reporter activity measured in the absence of FOXA1 co-expression. All experiments were conducted using eight replicates.