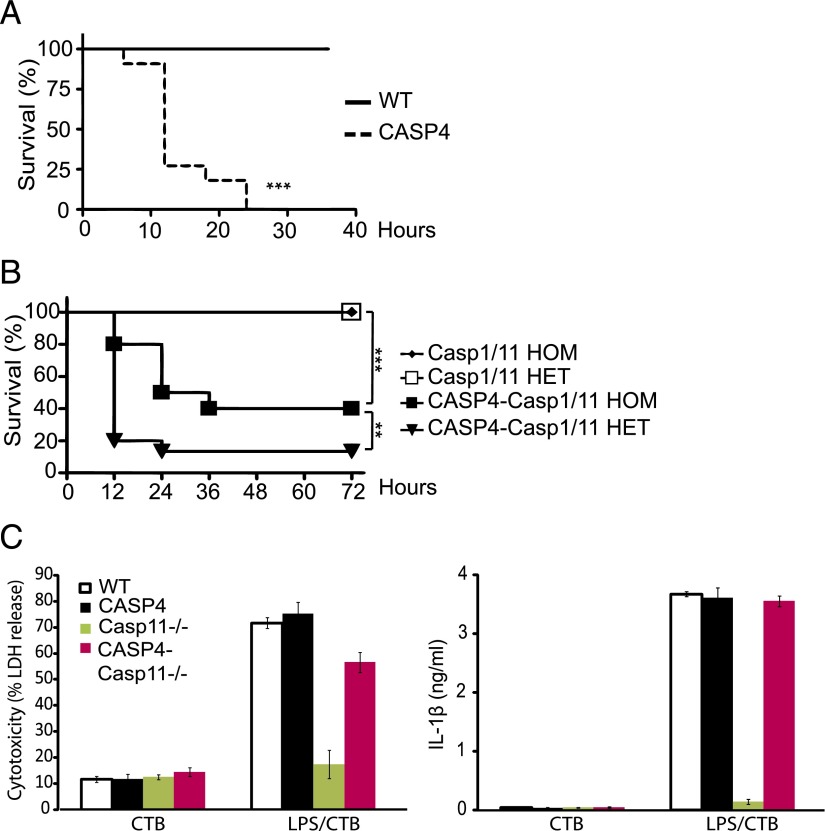
FIGURE 2.
Caspase-4 contributes to endotoxin-induced lethality. (A) LPS (5 mg/kg) was injected into WT and caspase-4 transgenic (CASP4) mice (n = 11/genotype), and survival was monitored every 6 h for the first 2 d and afterward once a day for 7 d. Results for the first 36 h are shown. All WT animals survived for the entire period. (B) LPS (10 mg/kg) was injected into mice, and survival was monitored every 12 h for up to 7 d. The first 72 h are shown (n = 10–17/genotype). The Casp1/11 homozygous (HOM) and heterozygous (HET) animals survived for the entire period. For (A) and (B), Kaplan-Meier survival tests were used for statistical analysis. (C) Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity and IL-1β secretion were measured 24 h after treating BMDMs from the indicated genotypes with cholera toxin B (CTB) (20 μg/ml) alone or together with ultrapure LPS (105 EU) derived from O111:B4 E. coli serotype. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.