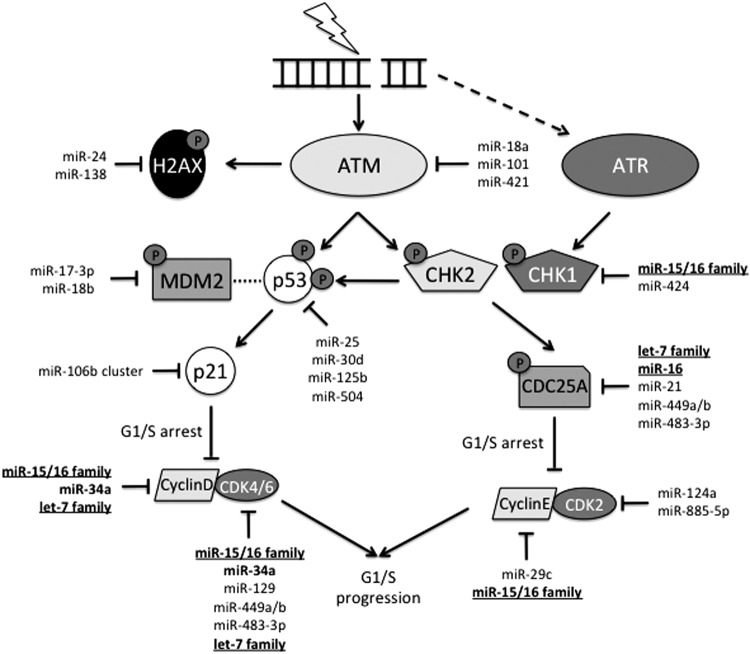
FIG. 4.
G1/S cell cycle checkpoint activation in response to radiation-induced DNA damage. IR induces DNA DSBs. ATM and ATR are recruited to sites of DNA damage, but ATM is specific for DSBs. ATM activates several down-stream mediators by phosphorylation, including H2AX, p53, and the CHK proteins, typically CHK2. Activated CHK2 phosphorylates CDC25A, targeting it for degradation. In the absence of CDC25A, Cyclin E and CDK2 are impaired, resulting in cell cycle arrest. CHK2 is also capable of activating p53 by phosphorylation. Concurrently, activated p53 is unable to bind to MDM2 (indicated by dotted line), leading to its accumulation. Accumulation of p53 stimulates p21 expression. p21 binds to both cyclin/CDK complexes and inhibits them from promoting progression through the cell cycle. miRNAs regulate almost every member of this checkpoint. Bold miRNAs indicate multiple targets within the pathway. Underlined miRNA families are seen throughout the DDR. Dotted arrow indicates limited secondary activation of ATR in response to DSBs. ATM, ataxia telangiectasia mutated; ATR, ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3 related; CDK, cyclin-dependent kinase.