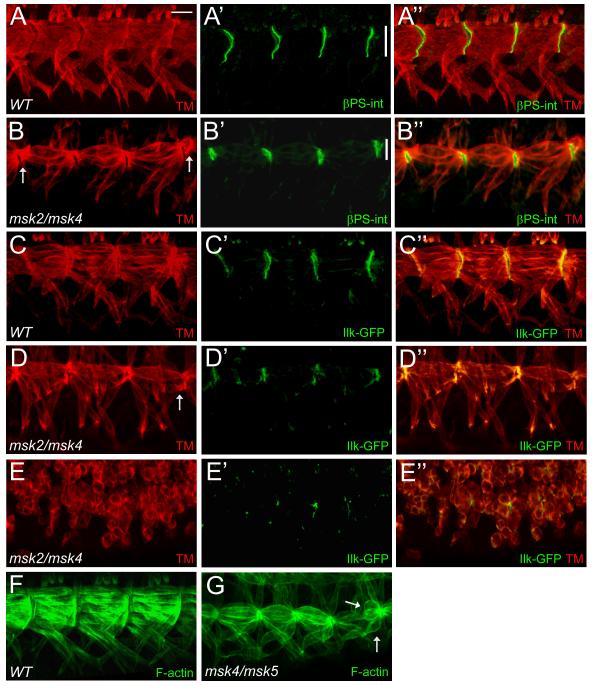
Figure 5. Components of integrin-mediated adherens junctions localize to the correct positions in msk mutant embryos.
(A-G) Immunofluorescent stainings of stage 17 embryos. Ventral musculature with anterior to the left and dorsal up. (A-B”) βPS-integrin staining in WT embryos localizes to the ends of muscles where they form contacts with tendon cells (A-A”). Msk mutants have correctly positioned, but smaller muscle attachment sites (compare vertical white bars) as demonstrated by βPS-int staining (B’-B”). (C-D”) Ilk-GFP also localizes to muscle attachment sites in WT (C’-C”). In msk mutants, Ilk-GFP is present at the correct place, although altered in size, in embryos that exhibit mild (D’-D”) or severe (E’-E”) muscle attachment defects. (F, G) Phalloidin labeling reveals F-actin filaments that span each muscle and accumulate at the ends of muscles in both WT (F) and msk (G) mutants. Arrows point out muscles that have detached. Scale bar: 20 μm.