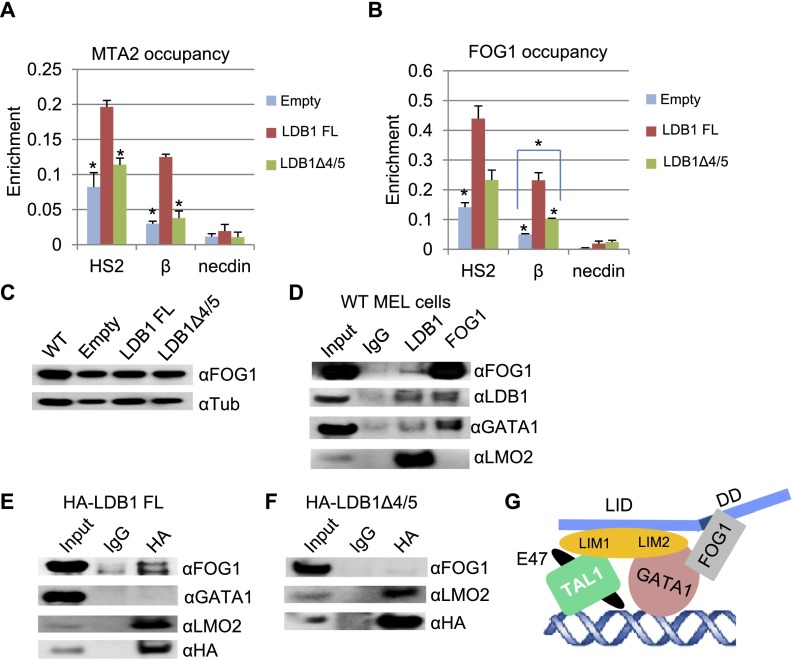
Figure 6.
Interaction between the LDB1 DD and FOG1. ChIP was performed with chromatin from induced LDB1 knockdown MEL cells expressing LDB1 FL or LDB1Δ4/5 or with an empty vector. Antibodies were against MTA2 (A) or FOG1 (B). Necdin served as a negative control. Error bars indicate SEM; n = 3. Values are compared with the value for LDB1 FL. (*) P < 0.05 by Student’s t-test. (C) Western blots of protein extracts from induced wild-type (WT) MEL cells and LDB1 knockdown MEL cell lines with an empty vector or expressing LDB1 FL or LDB1Δ4/5 with FOG1 antibodies. α-Tubulin served as a loading control. (D) Immunoprecipitation was performed with antibodies to LDB1 or FOG1 using nuclear extracts from induced wild-type MEL cells. Immunoprecipitation material was analyzed by Western blot with LDB1, FOG1, GATA1, and LMO2 antibodies. (E,F) Immunoprecipitation was performed with an HA antibody and nuclear extracts from induced LDB1 knockdown MEL cells expressing LDB1 FL (E) or LDB1 DDΔ4/5 (F). Immunoprecipitation material was analyzed by Western blot with FOG1, GATA1, and LMO2 antibodies. HA antibodies served as a positive control. (G) A model depicting protein–protein interactions within the LDB1 complex, including FOG1. Colored shapes representing factors are depicted as touching when such interaction is supported by biochemical and/or structural data (see the text). LMO2 N-terminal LIM1 and C-terminal LIM2 regions are indicated. The DD4/5 location in LDB1 is shaded.