Figure 3.
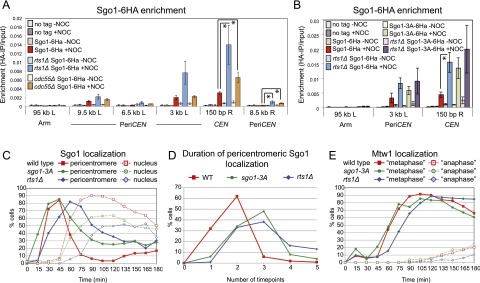
Association with PP2ARts1 is required for timely Sgo1 removal from the pericentromere. (A) Pericentromeric Sgo1 levels are regulated by Rts1 and Cdc55. Wild-type (AM6390), rts1Δ (AM8859), and cdc55Δ (AM8957) cells carrying SGO1-6HA and pMET3-CDC20 and a no tag pMET3-CDC20 control (AM2508) were arrested in metaphase in the presence or absence of microtubules as described in Figure 1G, and anti-HA ChIP was performed followed by qPCR with primer sets at the indicated locations on chromosome IV. The average of four experimental repeats is shown, with error bars representing standard error. Student’s t-test was used to calculate confidence values. (*) P < 0.05. (B) Interaction with PP2A is required to control Sgo1 levels on the centromere. Wild-type and rts1Δ cells carrying SGO1-6HA (AM6390 and AM8859) or SGO1-3A-6HA (AM10143 and AM11902) and pMET3-CDC20 together with a no tag control (AM2508) were grown and processed for ChIP-qPCR as described in A. The average of three experimental replicates are shown, with error bars representing standard error. (C,D) Sgo1 removal from the pericentromere is delayed in the absence of associated PP2ARts1. Wild-type (AM9233) or rts1Δ (AM9735) cells producing SGO1-yeGFP and SGO1-3A-yeGFP (AM9873) cells, all carrying pMET3-CDC20 and MTW1-tdTomato, were released from a G1 arrest on a microfluidics plate, and images were grabbed every 15 min. (C) Sgo1 localization was scored in at least 150 cells from each time point. (D) The number of frames in which pericentromeric Sgo1 signal was observed was scored for 100 cells per strain. (E) Bilobed Mtw1-tdTomato signal was scored in at least 150 cells as a marker of cell cycle progression.
