Figure 5. Effects of removal of extracellular Ca2+ on intracellular Ca2+ in intact human bronchi.
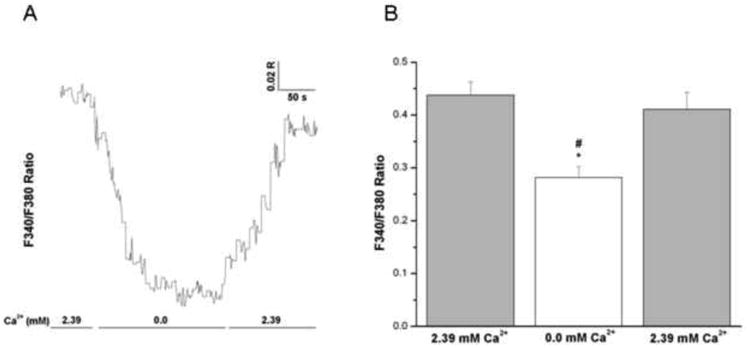
(A) Representative trace showing the effect of removal and reintroduction of extracellular Ca2+ on global [Ca2+]i levels in an intact human bronchial segment superfused in vitro. Notice the decrease in 340/380 ratio upon removal of extracellular Ca2+ and the subsequent increase in the 340/380 ratio upon the reintroduction of extracellular Ca2+. Similar results were obtained in 4 separate experiments. (B) Histogram showing the average of all experiments demonstrating a significant decrease in global [Ca2+]i levels correspondent with removal of Ca2+ from the extracellular medium in intact human bronchi, * P < 0.01. Upon reintroduction of extracellular Ca2+ there is a significant increase in global [Ca2+]i when compared to removal of Ca2+ from the extracellular medium, # P < 0.05. Data are represented as mean ± SE. Mean of 4 experiments, with tissue from 4 individuals.
