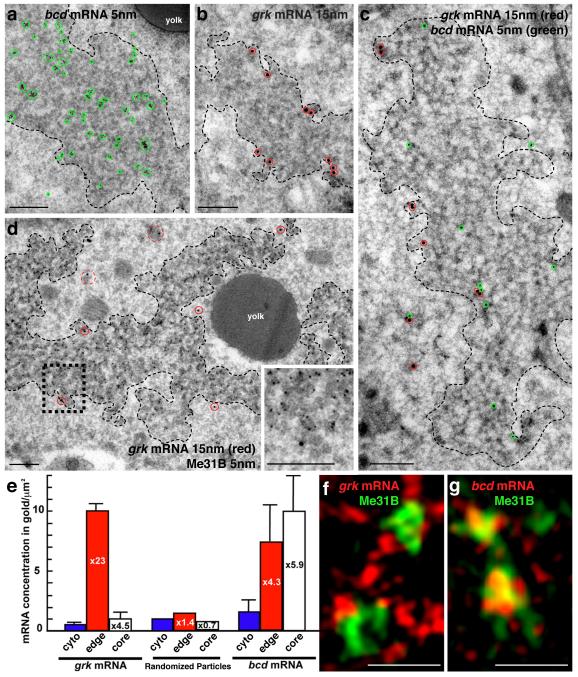
Figure 1. Differential association of bcd and grk with P bodies.
(a-d) mRNA detection at the dorsoanterior corner (for orientation, see Fig. 2a) by ISH-IEM on wild-type (WT) ultra-thin frozen sections of stage 9 oocytes. (a) bcd mRNA (5nm, green circles) is present both inside and at the edge of electron dense P bodies (dashed black line). Gold particles here cluster due to the use of a bridging antibody. (b) grk mRNA (15nm, red circles) is enriched at the edge of P bodies (dashed black line). (c) bcd mRNA (5nm, green circles) and grk mRNA (15nm, red circles) can associate with the same P body but bcd is enriched inside. (d) grk mRNA (15nm, red circles) docks at the edge of the P body (black dashed box magnified, inset bottom right), just outside of the Me31B dense core region (5nm gold), while grk transport particles, as described in Delanoue et. al., 2007(7), are detected in the cytoplasm at a short distance from the P body (15nm, red dashed circles). (e) mRNA density (gold/um2) in the P body sub-regions when compared to the surrounding cytoplasm. For comparison, randomized particles were analyzed in an identical way to RNAs. Error bars show SEM of gold density per scan (grk n=13, bcd n=11). (f,g) Fixed Me31B::GFP stage 8/9 expressing oocytes imaged using the OMX structured illumination super-resolution mode (3D-SIM) with double labeling of either (f) grk*mCherry, that mainly interdigitates with Me31B (green) while showing some colocalization at the edge (yellow) or (g) bcd*RFP grk mRNA (red), that shows significant colocalization (yellow) with Me31B (green). Scale bars, 200nm (a-d); 0.5μm (f, g).